Bhutan :: South Asia
Introduction
Background:
Following Britain's victory in the 1865 Duar War, Britain and Bhutan signed the Treaty of Sinchulu, under which Bhutan would receive an annual subsidy in exchange for ceding land to British India. Ugyen WANGCHUCK - who had served as the de facto ruler of an increasingly unified Bhutan and had improved relations with the British toward the end of the 19th century - was named king in 1907. Three years later, a treaty was signed whereby the British agreed not to interfere in Bhutanese internal affairs, and Bhutan allowed Britain to direct its foreign affairs. Bhutan negotiated a similar arrangement with independent India in 1949. The Indo-Bhutanese Treaty of Friendship returned to Bhutan a small piece of the territory annexed by the British, formalized the annual subsidies the country received, and defined India's responsibilities in defense and foreign relations. Under a succession of modernizing monarchs beginning in the 1950s, Bhutan joined the UN in 1971 and slowly continued its engagement beyond its borders.
++ In 2005, King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK unveiled the draft of Bhutan's first constitution - which introduced major democratic reforms - and held a national referendum for its approval. The King abdicated the throne in 2006 in favor of his son, Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK. In 2007, India and Bhutan renegotiated their treaty, eliminating the clause that stated that Bhutan would be "guided by" India in conducting its foreign policy, although Thimphu continues to coordinate closely with New Delhi. In 2008, Bhutan held its first parliamentary election in accordance with the constitution. Bhutan experienced a peaceful turnover of power following a parliamentary election in 2013, which resulted in the defeat of the incumbent party. In 2018, the incumbent party again lost the parliamentary election. Of the more than 100,000 ethnic Nepali - predominantly Lhotshampa - refugees who fled or were forced out of Bhutan in the 1990s, about 6,500 remain displaced in Nepal.
Geography
Location:
Southern Asia, between China and India
Geographic coordinates:
27 30 N, 90 30 E
Map references:
Asia
Area:
total:
38,394 sq km
land:
38,394 sq km
water:
0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 136
Area - comparative:
slightly larger than Maryland; about one-half the size of Indiana
Land boundaries:
total:
1,136 km
border countries (2):
China 477 km, India 659 km
Coastline:
0 km
(landlocked)
Maritime claims:
none (landlocked)
Climate:
varies; tropical in southern plains; cool winters and hot summers in central valleys; severe winters and cool summers in Himalayas
Terrain:
mostly mountainous with some fertile valleys and savanna
Elevation:
mean elevation:
2,220 m
lowest point:
Drangeme Chhu 97 m
highest point:
Gangkar Puensum 7,570 m
Natural resources:
timber, hydropower, gypsum, calcium carbonate
Land use:
agricultural land:
13.6%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
2.6%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
0.3%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent pasture:
10.7%
(2011 est.)
forest:
85.5%
(2011 est.)
other:
0.9%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
320 sq km
(2012)
Natural hazards:
violent storms from the Himalayas are the source of the country's Bhutanese name, which translates as Land of the Thunder Dragon; frequent landslides during the rainy season
Environment - current issues:
soil erosion; limited access to potable water; wildlife conservation; industrial pollution; waste disposal
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
Geography - note:
landlocked; strategic location between China and India; controls several key Himalayan mountain passes
People and Society
Population:
782,318
(July 2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
Nationality:
noun:
Bhutanese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Bhutanese
Ethnic groups:
Ngalop (also known as Bhote) 50%, ethnic Nepali 35% (predominantly Lhotshampas), indigenous or migrant tribes 15%
Languages:
Sharchhopka 28%, Dzongkha (official) 24%, Lhotshamkha 22%, other 26% (includes foreign languages)
(2005 est.)
Religions:
Lamaistic Buddhist 75.3%, Indian- and Nepali-influenced Hinduism 22.1%, other 2.6%
(2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years:
24.52%
(male 98,113/female 93,740)
15-24 years:
17.77%
(male 70,768/female 68,211)
25-54 years:
44.72%
(male 184,500/female 165,374)
55-64 years:
6.39%
(male 26,714/female 23,280)
65 years and over:
6.6%
(male 26,797/female 24,821)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
45.1
youth dependency ratio:
36.1
elderly dependency ratio:
9
potential support ratio:
11.1
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
29.1 years
male:
29.6 years
female:
28.6 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
Population growth rate:
1.02%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
Birth rate:
16.3 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
Death rate:
6.3 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
Net migration rate:
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
Urbanization:
urban population:
42.3% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
2.98% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
203,000 THIMPHU (capital)
(2018)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
1.04 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
1.12 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
1.15 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.08 male(s)/female
total population:
1.08 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Maternal mortality rate:
183 deaths/100,000 live births
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
Infant mortality rate:
total:
27 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
27.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
27 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
72.1 years
male:
71 years
female:
73.2 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
Total fertility rate:
1.82 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
Contraceptive prevalence rate:
65.6%
(2010)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban:
99.3% of population
rural:
100% of population
total:
99.7% of population
unimproved:
urban:
0.7% of population
rural:
0% of population
total:
0.3% of population
(2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure:
3.2%
(2017)
Physicians density:
0.4 physicians/1,000 population
(2017)
Hospital bed density:
1.7 beds/1,000 population
(2012)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban:
87.5% of population
rural:
72.1% of population
total:
78.3% of population
unimproved:
urban:
12.5% of population
rural:
27.9% of population
total:
21.7% of population
(2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
0.3%
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 84
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
1,300
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 140
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
<100
(2018)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:
6.4%
(2016)
country comparison to the world: 167
Children under the age of 5 years underweight:
12.7%
(2010)
country comparison to the world: 49
Education expenditures:
6.9% of GDP
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 15
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
66.6%
male:
75%
female:
57.1%
(2017)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total:
13 years
male:
13 years
female:
14 years
(2018)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total:
10.7%
male:
8.2%
female:
12.7%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 119
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
Kingdom of Bhutan
conventional short form:
Bhutan
local long form:
Druk Gyalkhap
local short form:
Druk Yul
etymology:
named after the Bhotia, the ethnic Tibetans who migrated from Tibet to Bhutan; "Bod" is the Tibetan name for their land; the Bhutanese name "Druk Yul" means "Land of the Thunder Dragon"
Government type:
constitutional monarchy
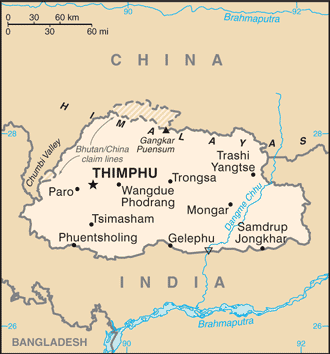
Capital:
name:
Thimphu
geographic coordinates:
27 28 N, 89 38 E
time difference:
UTC+6 (11 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the origins of the name are unclear; the traditional explanation, dating to the 14th century, is that "thim" means "dissolve" and "phu" denotes "high ground" to express the meaning of "dissolving high ground," in reference to a local deity that dissolved before a traveler's eyes, becoming a part of the rock on which the present city stands
Administrative divisions:
20 districts (dzongkhag, singular and plural); Bumthang, Chhukha, Dagana, Gasa, Haa, Lhuentse, Mongar, Paro, Pemagatshel, Punakha, Samdrup Jongkhar, Samtse, Sarpang, Thimphu, Trashigang, Trashi Yangtse, Trongsa, Tsirang, Wangdue Phodrang, Zhemgang
Independence:
17 December 1907 (became a unified kingdom under its first hereditary king); 8 August 1949 (Treaty of Friendship with India maintains Bhutanese independence)
National holiday:
National Day (Ugyen WANGCHUCK became first hereditary king), 17 December (1907)
Constitution:
history:
previous governing documents were various royal decrees; first constitution drafted November 2001 to March 2005, ratified 18 July 2008
amendments:
proposed as a motion by simple majority vote in a joint session of Parliament; passage requires at least a three-fourths majority vote in a joint session of the next Parliament and assent by the king
Legal system:
civil law based on Buddhist religious law
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
no
citizenship by descent only:
the father must be a citizen of Bhutan
dual citizenship recognized:
no
residency requirement for naturalization:
10 years
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state:
King Jigme Khesar Namgyel WANGCHUCK (since 14 December 2006); note - King Jigme Singye WANGCHUCK abdicated the throne on 14 December 2006 to his son
head of government:
Prime Minister Lotay TSHERING (since 7 November 2018)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers or Lhengye Zhungtshog members nominated by the monarch in consultation with the prime minister and approved by the National Assembly; members serve 5-year terms
elections/appointments:
the monarchy is hereditary but can be removed by a two-thirds vote of Parliament; leader of the majority party in Parliament is nominated as the prime minister, appointed by the monarch
Legislative branch:
description:
bicameral Parliament or Chi Tshog consists of: non-partisan National Council or Gyelyong Tshogde (25 seats; 20 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 5 members appointed by the king; members serve 5-year terms) ++ National Assembly or Tshogdu (47 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections: National Council election last held on 20 April 2018 (next to be held in 2023) ++ National Assembly - first round held on 15 September 2018 and second round held on 18 October 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
election results: National Council - seats by party - independent 20 (all candidates ran as independents); composition - men 23, women 2, percent of women 8% ++ National Assembly - first round - percent of vote by party - DNT 31.9%, DPT 30.9%, PDP 27.4%, BKP 9.8%; second round - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - DNT 30, DPT 17; composition - men 40, women 7, percent of women 14.9%; note - total Parliament percent of women 12.5%
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and 4 associate justices); note - the Supreme Court has sole jurisdiction in constitutional matters
judge selection and term of office:
Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the monarch upon the advice of the National Judicial Commission, a 4-member body to include the Legislative Committee of the National Assembly, the attorney general, the Chief Justice of Bhutan and the senior Associate Justice of the Supreme Court; other judges (drangpons) appointed by the monarch from among the High Court judges selected by the National Judicial Commission; chief justice serves a 5-year term or until reaching age 65 years, whichever is earlier; the 4 other judges serve 10-year terms or until age 65, whichever is earlier
subordinate courts:
High Court (first appellate court); District or Dzongkhag Courts; sub-district or Dungkhag Courts
Political parties and leaders:
Bhutan Kuen-Nyam Party or BKP ++ Bhutan Peace and Prosperity Party (Druk Phuensum Tshogpa) or DPT [Pema GYAMTSHO] (Druk Chirwang Tshogpa or DCT merged with DPT in March 2018) ++ People's Democratic Party or PDP [Tshering TOBGAY] ++ United Party of Bhutan (Druk Nyamrup Tshogpa) or DNT [Lotay TSHERING]
International organization participation:
ADB, BIMSTEC, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer)
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
none; the Permanent Mission to the UN for Bhutan has consular jurisdiction in the US; the permanent representative to the UN is Doma TSHERING (since 13 September 2017); address: 343 East 43rd Street, New York, NY 10017; telephone [1] (212) 682-2268; FAX [1] (212) 661-0551
consulate(s) general:
New York
Diplomatic representation from the US:
none; frequent informal contact is maintained via the US embassy in New Delhi (India) and Bhutan's Permanent Mission to the UN
Flag description:
divided diagonally from the lower hoist-side corner; the upper triangle is yellow and the lower triangle is orange; centered along the dividing line is a large black and white dragon facing away from the hoist side; the dragon, called the Druk (Thunder Dragon), is the emblem of the nation; its white color stands for purity and the jewels in its claws symbolize wealth; the background colors represent spiritual and secular powers within Bhutan: the orange is associated with Buddhism, while the yellow denotes the ruling dynasty
National symbol(s):
thunder dragon known as Druk Gyalpo; national colors: orange, yellow
National anthem:
name:
"Druk tsendhen" (The Thunder Dragon Kingdom)
lyrics/music:
Gyaldun Dasho Thinley DORJI/Aku TONGMI
note: adopted 1953
Economy
Economic overview:
Bhutan's small economy is based largely on hydropower, agriculture, and forestry, which provide the main livelihood for more than half the population. Because rugged mountains dominate the terrain and make the building of roads and other infrastructure difficult and expensive, industrial production is primarily of the cottage industry type. The economy is closely aligned with India's through strong trade and monetary links and is dependent on India for financial assistance and migrant laborers for development projects, especially for road construction. Bhutan signed a pact in December 2014 to expand duty-free trade with Bangladesh.
++ Multilateral development organizations administer most educational, social, and environment programs, and take into account the government's desire to protect the country's environment and cultural traditions. For example, the government is cautious in its expansion of the tourist sector, restricing visits to environmentally conscientious tourists. Complicated controls and uncertain policies in areas such as industrial licensing, trade, labor, and finance continue to hamper foreign investment.
++ Bhutan's largest export - hydropower to India - could spur sustainable growth in the coming years if Bhutan resolves chronic delays in construction. Bhutan's hydropower exports comprise 40% of total exports and 25% of the government's total revenue. Bhutan currently taps only 6.5% of its 24,000-megawatt hydropower potential and is behind schedule in building 12 new hydropower dams with a combined capacity of 10,000 megawatts by 2020 in accordance with a deal signed in 2008 with India. The high volume of imported materials to build hydropower plants has expanded Bhutan's trade and current account deficits. Bhutan also signed a memorandum of understanding with Bangladesh and India in July 2017 to jointly construct a new hydropower plant for exporting electricity to Bangladesh.
GDP real growth rate:
7.4%
(2017 est.)
7.3%
(2016 est.)
6.2%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
5.8%
(2017 est.)
7.6%
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
Credit ratings:
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$7.205 billion
(2017 est.)
$6.71 billion
(2016 est.)
$6.252 billion
(2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$2.405 billion
(2017 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$9,000
(2017 est.)
$8,500
(2016 est.)
$8,000
(2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 123
Gross national saving:
40.4% of GDP
(2017 est.)
33.3% of GDP
(2016 est.)
32% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
16.2%
(2017 est.)
industry:
41.8%
(2017 est.)
services:
42%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
58%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
16.8%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
47.2%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
0%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
26%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-48%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
66.0
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
rice, corn, root crops, citrus; dairy products, eggs
Industries:
cement, wood products, processed fruits, alcoholic beverages, calcium carbide, tourism
Industrial production growth rate:
6.3%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
Labor force:
397,900
(2017 est.)
note: major shortage of skilled labor
country comparison to the world: 159
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
58%
industry:
20%
services:
22%
(2015 est.)
Unemployment rate:
3.2%
(2017 est.)
3.2%
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
Population below poverty line:
12%
(2012 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
2.8%
highest 10%:
30.6%
(2012)
Budget:
revenues:
655.3 million
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
737.4 million
(2017 est.)
note: the Government of India finances nearly one-quarter of Bhutan's budget expenditures
Taxes and other revenues:
27.2% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-3.4% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
Public debt:
106.3% of GDP
(2017 est.)
114.2% of GDP
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
Fiscal year:
1 July - 30 June
Current account balance:
-$547 million
(2017 est.)
-$621 million
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
Exports:
$554.6 million
(2017 est.)
$495.3 million
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 173
Exports - partners:
India 95.3%
(2017)
Exports - commodities:
electricity (to India), ferrosilicon, cement, cardamom, calcium carbide, steel rods/bars, dolomite, gypsum
Imports:
$1.025 billion
(2017 est.)
$1.03 billion
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
Imports - commodities:
fuel and lubricants, airplanes, machinery and parts, rice, motor vehicles
Imports - partners:
India 89.5%
(2017)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$1.206 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$1.127 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
Debt - external:
$2.671 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$2.355 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
Exchange rates:
ngultrum (BTN) per US dollar -
64.97
(2017 est.)
67.2
(2016 est.)
67.2
(2015 est.)
64.15
(2014 est.)
61.03
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access:
electrification - total population:
100%
(2020)
Electricity - production:
7.883 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 110
Electricity - consumption:
2.184 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
Electricity - exports:
5.763 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
Electricity - imports:
84 million kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 101
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
1.632 million kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
1% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
99% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
Crude oil - production:
0 bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
Crude oil - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
Crude oil - imports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
Crude oil - proved reserves:
0 bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
Refined petroleum products - production:
0 bbl/day
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 120
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
3,000 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
Refined petroleum products - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 132
Refined petroleum products - imports:
3,120 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
Natural gas - production:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
Natural gas - consumption:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
Natural gas - imports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
Natural gas - proved reserves:
0 cu m
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
604,900 Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
21,916
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
2.83
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
740,026
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
95.56
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
4G platforms now gaining traction; 4G/WiMAX networks now cover well over half of the country; fixed broadband penetration remains very low, due to the preeminence of the mobile platform; low to moderate growth is expected from this small base with a maturing mobile subscriber market
(2020)
domestic:
3 to 100 fixed-line, 96 to 100 mobile cellular; domestic service inadequate, notably in rural areas
(2019)
international:
country code - 975; international telephone and telegraph service via landline and microwave relay through India; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
state-owned TV station established in 1999; cable TV service offers dozens of Indian and other international channels; first radio station, privately launched in 1973, is now state-owned; 5 private radio stations are currently broadcasting
(2012)
Internet country code:
.bt
Internet users:
total:
368,714
percent of population:
48.11%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
10,802
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
1
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
Transportation
National air transport system:
number of registered air carriers:
2
(2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers:
6
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers:
275,849
(2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers:
690,000
mt-km
(2018)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
A5
(2016)
Airports:
2
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 196
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
2
(2017)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
(2017)
914 to 1,523 m:
1
(2017)
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
1
(2012)
914 to 1,523 m:
1
(2012)
Roadways:
total:
12,205 km
(2017)
urban:
437 km
(2017)
country comparison to the world: 132
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Royal Bhutan Army (includes Royal Bodyguard, plus militia); Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs: Royal Bhutan Police
(2019)
note: Bhutan does not have an air force; India is responsible for military training, arms supplies, and the air defense of Bhutan
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Royal Bhutan Army has approximately 8,000 personnel
(2019 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
India has provided most of the Royal Bhutan Army's equipment, although the only recorded delivery of military equipment to Bhutan since 2010 was from France
(2019 est.)
Military service age and obligation:
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; militia training is compulsory for males aged 20-25, over a 3-year period
(2012)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
lacking any treaty describing the boundary, Bhutan and China continue negotiations to establish a common boundary alignment to resolve territorial disputes arising from substantial cartographic discrepancies, the most contentious of which lie in Bhutan's west along China's Chumbi salient