Kuwait :: Middle East
Introduction
Background:
Kuwait has been ruled by the AL-SABAH dynasty since the 18th century. The threat of Ottoman invasion in 1899 prompted Amir Mubarak AL-SABAH to seek protection from Britain, ceding foreign and defense responsibility to Britain until 1961, when the country attained its independence. Kuwait was attacked and overrun by Iraq in August 1990. Following several weeks of aerial bombardment, a US-led UN coalition began a ground assault in February 1991 that liberated Kuwait in four days. In 1992, the Amir reconstituted the parliament that he had dissolved in 1986. Amid the 2010-11 uprisings and protests across the Arab world, stateless Arabs, known as Bidoon, staged small protests in early 2011 demanding citizenship, jobs, and other benefits available to Kuwaiti nationals. Other demographic groups, notably Islamists and Kuwaitis from tribal backgrounds, soon joined the growing protest movements, which culminated in late 2011 with the resignation of the prime minister amidst allegations of corruption. Demonstrations renewed in late 2012 in response to an amiri decree amending the electoral law that lessened the voting power of the tribal blocs. ++ An opposition coalition of Sunni Islamists, tribal populists, and some liberals, largely boycotted legislative elections in 2012 and 2013, which ushered in a legislature more amenable to the government's agenda. Faced with the prospect of painful subsidy cuts, oppositionists and independents actively participated in the November 2016 election, winning nearly half of the seats but a cohesive opposition alliance largely ceased to exist with the 2016 election and the opposition became increasingly factionalized. Since coming to power in 2006, the Amir has dissolved the National Assembly on seven occasions (the Constitutional Court annulled the Assembly elections in June 2012 and again in June 2013) and shuffled the cabinet over a dozen times, usually citing political stagnation and gridlock between the legislature and the government.
Geography
Location:
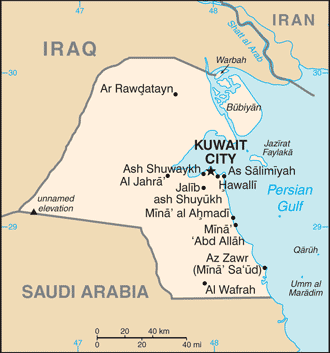
Middle East, bordering the Persian Gulf, between Iraq and Saudi Arabia
Geographic coordinates:
29 30 N, 45 45 E
Map references:
Middle East
Area:
total:
17,818 sq km
land:
17,818 sq km
water:
0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 157
Area - comparative:
slightly smaller than New Jersey
Land boundaries:
total:
475 km
border countries (2):
Iraq 254 km, Saudi Arabia 221 km
Coastline:
499 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea:
12
nm
Climate:
dry desert; intensely hot summers; short, cool winters
Terrain:
flat to slightly undulating desert plain
Elevation:
mean elevation:
108 m
lowest point:
Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
3.6 km W. of Al-Salmi Border Post 300 m
Natural resources:
petroleum, fish, shrimp, natural gas
Land use:
agricultural land:
8.5%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
0.6%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
0.3%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent pasture:
7.6%
(2011 est.)
forest:
0.4%
(2011 est.)
other:
91.1%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
105 sq km
(2012)
Population distribution:
densest settlement is along the Persian Gulf, particularly in Kuwait City and on Bubiyan Island; significant population threads extend south and west along highways that radiate from the capital, particularly in the southern half of the country
Natural hazards:
sudden cloudbursts are common from October to April and bring heavy rain, which can damage roads and houses; sandstorms and dust storms occur throughout the year but are most common between March and August
Environment - current issues:
limited natural freshwater resources; some of world's largest and most sophisticated desalination facilities provide much of the water; air and water pollution; desertification; loss of biodiversity
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
Marine Dumping
Geography - note:
strategic location at head of Persian Gulf
People and Society
Population:
2,993,706
(July 2020 est.)
note: Kuwait's Public Authority for Civil Information estimates the country's total population to be 4,420,110 for 2019, with non-Kuwaitis accounting for nearly 70% of the population
country comparison to the world: 138
Nationality:
noun:
Kuwaiti(s)
adjective:
Kuwaiti
Ethnic groups:
Kuwaiti 30.4%, other Arab 27.4%, Asian 40.3%, African 1%, other .9% (includes European, North American, South American, and Australian)
(2018 est.)
Languages:
Arabic (official), English widely spoken
Religions:
Muslim (official) 74.6%, Christian 18.2%, other and unspecified 7.2%
(2013 est.)
note: data represent the total population; about 69% of the population consists of immigrants
Age structure:
0-14 years:
24.29%
(male 378,778/female 348,512)
15-24 years:
14.96%
(male 245,354/female 202,642)
25-54 years:
52.39%
(male 984,813/female 583,632)
55-64 years:
5.43%
(male 90,583/female 72,026)
65 years and over:
2.92%
(male 38,614/female 48,752)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
32.4
youth dependency ratio:
28.4
elderly dependency ratio:
4
potential support ratio:
24.9
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
29.7 years
male:
30.7 years
female:
27.9 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
Population growth rate:
1.27%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
Birth rate:
18 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
Death rate:
2.3 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 226
Net migration rate:
-3.3 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 180
Population distribution:
densest settlement is along the Persian Gulf, particularly in Kuwait City and on Bubiyan Island; significant population threads extend south and west along highways that radiate from the capital, particularly in the southern half of the country
Urbanization:
urban population:
100% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
1.78% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
3.115 million KUWAIT (capital)
(2020)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.09 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
1.21 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
1.69 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
1.26 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.79 male(s)/female
total population:
1.38 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Maternal mortality rate:
12 deaths/100,000 live births
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
Infant mortality rate:
total:
6.5 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
6.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
6.7 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 161
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
78.6 years
male:
77.2 years
female:
80.2 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
Total fertility rate:
2.26 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
Drinking water source:
improved:
total:
100% of population
unimproved:
total:
0% of population
(2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure:
5.3%
(2017)
Physicians density:
2.65 physicians/1,000 population
(2015)
Hospital bed density:
2 beds/1,000 population
(2017)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
total:
100% of population
unimproved:
total:
0% of population
(2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
<.1%
(2018 est.)
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
<1000
(2018 est.)
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
<100
(2018 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:
37.9%
(2016)
country comparison to the world: 11
Children under the age of 5 years underweight:
3%
(2014)
country comparison to the world: 101
Education expenditures:
NA
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
96.1%
male:
96.7%
female:
94.9%
(2018)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total:
15 years
male:
14 years
female:
16 years
(2015)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total:
15.4%
male:
9.4%
N/A
female:
30%
N/A
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
State of Kuwait
conventional short form:
Kuwait
local long form:
Dawlat al Kuwayt
local short form:
Al Kuwayt
etymology:
the name derives from the capital city, which is from Arabic "al-Kuwayt" a diminutive of "kut" meaning "fortress," possibly a reference to a small castle built on the current location of Kuwait City by the Beni Khaled tribe in the 17th century
Government type:
constitutional monarchy (emirate)
Capital:
name:
Kuwait City
geographic coordinates:
29 22 N, 47 58 E
time difference:
UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name derives from Arabic "al-Kuwayt" a diminutive of "kut" meaning "fortress," possibly a reference to a small castle built on the current location of Kuwait City by the Beni Khaled tribe in the 17th century
Administrative divisions:
6 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazah); Al Ahmadi, Al 'Asimah, Al Farwaniyah, Al Jahra', Hawalli, Mubarak al Kabir
Independence:
19 June 1961 (from the UK)
National holiday:
National Day, 25 February (1950)
Constitution:
history:
approved and promulgated 11 November 1962
amendments:
proposed by the amir or supported by at least one third of the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds consent of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the amir; constitutional articles on the initiation, approval, and promulgation of general legislation cannot be amended
Legal system:
mixed legal system consisting of English common law, French civil law, and Islamic sharia law
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
no
citizenship by descent only:
at least one parent must be a citizen of Kuwait
dual citizenship recognized:
no
residency requirement for naturalization:
not specified
Suffrage:
21 years of age and at least 20-year citizenship
Executive branch:
chief of state:
Amir NAWAF al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah (since 30 September 2020); Crown Prince Sheikh MESHAAL Al Ahmad Al Sabah, born in 1940, is the brother of Amir NAWAF al-Ahmad al-Jabir al-Sabah
head of government:
Prime Minister JABIR AL-MUBARAK al-Hamad al-Sabah (since 30 November 2011); First Deputy Prime Minister NASIR Sabah al-Ahmad al-Sabah (since 11 December 2017); Deputy Prime Ministers SABAH KHALID al-Hamid al-Sabah (since 13 December 2011), KHALID al-Jarrah al-Sabah (since 4 August 2013), Anas Khalid al-SALEH (since 4 August 2013); note - on 14 November 2019, the government of Prime Minister JABIR AL-MUBARAK al-Hamad al-Sabah resigned
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister, approved by the amir
elections/appointments:
amir chosen from within the ruling family, confirmed by the National Assembly; prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the amir; crown prince appointed by the amir and approved by the National Assembly
Legislative branch:
description:
unicameral National Assembly or Majlis al-Umma (65 seats; 50 members directly elected from 5 multi-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 15 ex-officio members (cabinet ministers) appointed by the amir; members serve 4-year terms)
elections:
last held on 5 December 2020 (next to be held in 2024)
election results:
all candidates ran as independents, though nearly half were oppositionists; composition - men 50, women 0, percent of women 0%
note: seats as of May 2019 - oppositionists and independents, including populists, Islamists, and liberals 25, pro-government loyalists 25; composition as of May 2019 for elected members only - men 49, women 1, percent of women 2%
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Constitutional Court (consists of 5 judges); Supreme Court or Court of Cassation (organized into several circuits, each with 5 judges)
judge selection and term of office:
all Kuwaiti judges appointed by the Amir upon recommendation of the Supreme Judicial Council, a consultative body comprised of Kuwaiti judges and Ministry of Justice officials
subordinate courts:
High Court of Appeal; Court of First Instance; Summary Court
Political parties and leaders:
none; the government does not recognize any political parties or allow their formation, although no formal law bans political parties
International organization participation:
ABEDA, AfDB (nonregional member), AFESD, AMF, BDEAC, CAEU, CD, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, Paris Club (associate), PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UN Security Council (temporary), UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador SALIM al-Abdallah al-Jabir al-Sabah (since 10 October 2001)
chancery:
2940 Tilden Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 966-0702
FAX:
[1] (202) 966-8468
consulate(s) general:
New York City
consulate(s):
Lost Angeles
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission:
Alina L. Romanowski (since 6 January 2020)
telephone:
[965] 2259-1001
embassy:
P.O. Box 77, Safat 13001
mailing address:
P. O. Box 77 Safat 13001 Kuwait; or PSC 1280 APO AE 09880-9000
FAX:
[965] 2538-6562
Flag description:
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), white, and red with a black trapezoid based on the hoist side; colors and design are based on the Arab Revolt flag of World War I; green represents fertile fields, white stands for purity, red denotes blood on Kuwaiti swords, black signifies the defeat of the enemy
National symbol(s):
golden falcon; national colors: green, white, red, black
National anthem:
name:
"Al-Nasheed Al-Watani" (National Anthem)
lyrics/music:
Ahmad MUSHARI al-Adwani/Ibrahim Nasir al-SOULA
note: adopted 1978; the anthem is only used on formal occasions
Economy
Economic overview:
Kuwait has a geographically small, but wealthy, relatively open economy with crude oil reserves of about 102 billion barrels - more than 6% of world reserves. Kuwaiti officials plan to increase production to 4 million barrels of oil equivalent per day by 2020. Petroleum accounts for over half of GDP, 92% of export revenues, and 90% of government income.
++ With world oil prices declining, Kuwait realized a budget deficit in 2015 for the first time more than a decade; in 2016, the deficit grew to 16.5% of GDP. Kuwaiti authorities announced cuts to fuel subsidies in August 2016, provoking outrage among the public and National Assembly, and the Amir dissolved the government for the seventh time in ten years. In 2017 the deficit was reduced to 7.2% of GDP, and the government raised $8 billion by issuing international bonds. Despite Kuwait's dependence on oil, the government has cushioned itself against the impact of lower oil prices, by saving annually at least 10% of government revenue in the Fund for Future Generations.
++ Kuwait has failed to diversify its economy or bolster the private sector, because of a poor business climate, a large public sector that employs about 74% of citizens, and an acrimonious relationship between the National Assembly and the executive branch that has stymied most economic reforms. The Kuwaiti Government has made little progress on its long-term economic development plan first passed in 2010. While the government planned to spend up to $104 billion over four years to diversify the economy, attract more investment, and boost private sector participation in the economy, many of the projects did not materialize because of an uncertain political situation or delays in awarding contracts. To increase non-oil revenues, the Kuwaiti Government in August 2017 approved draft bills supporting a Gulf Cooperation Council-wide value added tax scheduled to take effect in 2018.
GDP real growth rate:
-3.3%
(2017 est.)
2.2%
(2016 est.)
-1%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
1.5%
(2017 est.)
3.5%
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 89
Credit ratings:
Fitch rating:
AA
(2008)
Moody's rating:
A1
(2020)
Standard & Poors rating:
AA-
(2020)
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$262.665 billion
(2018 est.)
$289.7 billion
(2017 est.)
$259.433 billion
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$134.638 billion
(2019 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$33,087
(2018 est.)
$65,800
(2017 est.)
$33,334
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 53
Gross national saving:
35.4% of GDP
(2017 est.)
32.9% of GDP
(2016 est.)
37.1% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
0.4%
(2017 est.)
industry:
58.7%
(2017 est.)
services:
40.9%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
43.1%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
24.5%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
26.5%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
3.5%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
49.4%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-47%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
88.4
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
fish
Industries:
petroleum, petrochemicals, cement, shipbuilding and repair, water desalination, food processing, construction materials
Industrial production growth rate:
2.8%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
Labor force:
2.695 million
(2017 est.)
note: non-Kuwaitis represent about 60% of the labor force
country comparison to the world: 111
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
NA
industry:
NA
services:
NA
Unemployment rate:
1.1%
(2017 est.)
1.1%
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 12
Population below poverty line:
NA
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
NA
highest 10%:
NA
Budget:
revenues:
50.5 billion
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
62.6 billion
(2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
41.8% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 32
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-10% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 210
Public debt:
20.6% of GDP
(2017 est.)
9.9% of GDP
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
Fiscal year:
1 April - 31 March
Current account balance:
$7.127 billion
(2017 est.)
-$5.056 billion
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
Exports:
$84.825 billion
(2018 est.)
$89.098 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
Exports - partners:
South Korea 18.3%, China 17.4%, Japan 11.5%, India 11.2%, Singapore 6.3%, US 5.7%
(2017)
Exports - commodities:
oil and refined products, fertilizers
Imports:
$54.556 billion
(2018 est.)
$55.025 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
Imports - commodities:
food, construction materials, vehicles and parts, clothing
Imports - partners:
China 13.5%, US 13.3%, UAE 9.5%, Saudi Arabia 5.8%, Germany 5.4%, Japan 5%, India 4.7%, Italy 4.5%
(2017)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$33.7 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$31.13 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 48
Debt - external:
$47.24 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$38.34 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
Exchange rates:
Kuwaiti dinars (KD) per US dollar -
0.3049
(2020 est.)
0.3037
(2019 est.)
0.304
(2018 est.)
0.3009
(2014 est.)
0.2845
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access:
electrification - total population:
100%
(2020)
Electricity - production:
65.95 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
Electricity - consumption:
57.78 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
Electricity - exports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
Electricity - imports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
18.89 million kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
100% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 122
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
Crude oil - production:
2.807 million bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
Crude oil - exports:
479,700 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Crude oil - imports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
Crude oil - proved reserves:
101.5 billion bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
Refined petroleum products - production:
915,800 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
446,000 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
Refined petroleum products - exports:
705,500 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
Refined petroleum products - imports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 211
Natural gas - production:
17.1 billion cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
Natural gas - consumption:
21.72 billion cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
Natural gas - imports:
5.125 billion cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 35
Natural gas - proved reserves:
1.784 trillion cu m
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
106.5 million Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
368,305
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
12.46
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
5,147,990
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
174.16
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
the quality of service is excellent; new telephone exchanges provide a large capacity for new subscribers; trunk traffic is carried by microwave radio relay, coaxial cable, and open-wire and fiber-optic cable; a 4G LTE mobile-cellular telephone system operates throughout Kuwait; Internet access is available via 4G LTE connections for fixed and mobile users; high ownership of smart phone in Kuwait; one of the highest mobile penetration rates in the world; exploring 5G opportunities; improvements to fiber-broadband underway
(2020)
domestic:
fixed-line subscriptions are 12 per 100 and mobile-cellular stands at 174 per 100 subscriptions
(2019)
international:
country code - 965; landing points for the FOG, GBICS, MENA, Kuwait-Iran, and FALCON submarine cables linking Africa, the Middle East, and Asia; microwave radio relay to Saudi Arabia; satellite earth stations - 6 (3 Intelsat - 1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean, 1 Inmarsat - Atlantic Ocean, and 2 Arabsat)
(2019)
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
state-owned TV broadcaster operates 4 networks and a satellite channel; several private TV broadcasters have emerged; satellite TV available and pan-Arab TV stations are especially popular; state-owned Radio Kuwait broadcasts on a number of channels in Arabic and English; first private radio station emerged in 2005; transmissions of at least 2 international radio broadcasters are available
(2019)
Internet country code:
.kw
Internet users:
total:
2,904,801
percent of population:
99.6%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 99
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
103,821
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
4
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
Transportation
National air transport system:
number of registered air carriers:
2
(2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers:
44
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers:
6,464,847
(2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers:
392.36 million
mt-km
(2018)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
9K
(2016)
Airports:
7
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 169
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
4
(2019)
over 3,047 m:
1
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
914 to 1,523 m:
1
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
3
(2013)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
(2013)
under 914 m:
2
(2013)
Heliports:
4
(2013)
Pipelines:
261 km gas, 540 km oil, 57 km refined products
(2013)
Roadways:
total:
5,749 km
(2018)
paved:
4,887 km
(2018)
unpaved:
862 km
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 145
Merchant marine:
total:
154
by type:
general cargo 15, oil tanker 24, other 115
(2019)
country comparison to the world: 71
Ports and terminals:
major seaport(s):
Ash Shu'aybah, Ash Shuwaykh, Az Zawr (Mina' Sa'ud), Mina' 'Abd Allah, Mina' al Ahmadi
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Kuwaiti Armed Forces: Kuwaiti Land Forces (KLF), Kuwaiti Navy, Kuwaiti Air Force (Al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Kuwaitiya; includes Kuwaiti Air Defense Force, KADF), 25th Commando Brigade, and the Kuwait Emiri Guard Brigade; Kuwaiti National Guard (KNG); Coast Guard (Ministry of Interior)
(2019)
note: the Kuwait Emiri Guard Authority and the 25th Commando Brigade exercise independent command authority within the Kuwaiti Armed Forces, although activities such as training and equipment procurement are often coordinated with the other services; the KNG possesses an independent command structure, equipment inventory, and logistics corps separate from the Ministry of Defense, the regular armed services, and the Ministry of Interior
Military expenditures:
5.6% of GDP
(2019)
5.1% of GDP
(2018)
5.6% of GDP
(2017)
5.8% of GDP
(2016)
5% of GDP
(2015)
country comparison to the world: 5
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Kuwaiti Armed Forces have approximately 17,000 active personnel (12,500 Army; 2,000 Navy; 2,500 Air Force); est. 6,500 National Guard; note – Army figures include the Kuwait Emiri Guard Authority (est. 500) and the 25th Commando Brigade (N/A)
(2019 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
the inventory of the Kuwaiti Armed Forces consists of a range of European- and US-sourced weapons systems; the US is the leading supplier of arms to Kuwait since 2010
(2019 est.)
Military service age and obligation:
17-21 years of age for voluntary military service; Kuwait reintroduced one-year mandatory service for men aged 18-35 in May 2017 after having suspended conscription in 2001; service is divided in two phases – four months for training and eight months for military service
(2018)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
Kuwait and Saudi Arabia continue negotiating a joint maritime boundary with Iran; no maritime boundary exists with Iraq in the Persian Gulf
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
stateless persons:
92,020 (2019); note - Kuwait's 1959 Nationality Law defined citizens as persons who settled in the country before 1920 and who had maintained normal residence since then; one-third of the population, descendants of Bedouin tribes, missed the window of opportunity to register for nationality rights after Kuwait became independent in 1961 and were classified as bidun (meaning "without"); since the 1980s Kuwait's bidun have progressively lost their rights, including opportunities for employment and education, amid official claims that they are nationals of other countries who have destroyed their identification documents in hopes of gaining Kuwaiti citizenship; Kuwaiti authorities have delayed processing citizenship applications and labeled biduns as "illegal residents," denying them access to civil documentation, such as birth and marriage certificates
Trafficking in persons:
current situation:
Kuwait is a destination country for men and women subjected to forced labor and, to a lesser degree, forced prostitution; men and women migrate from South and Southeast Asia, Egypt, the Middle East, and increasingly Africa to work in Kuwait, most of them in the domestic service, construction, and sanitation sectors; although most of these migrants enter Kuwait voluntarily, upon arrival some are subjected to conditions of forced labor by their sponsors and labor agents, including debt bondage; Kuwait's sponsorship law restricts workers' movements and penalizes them for running away from abusive workplaces, making domestic workers particularly vulnerable to forced labor in private homes
tier rating:
Tier 3 - Kuwait does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making sufficient efforts to do so; although investigations into visa fraud rings lead to the referral of hundreds of people for prosecution, including complicit officials, the government has not prosecuted or convicted any suspected traffickers; authorities made no effort to enforce the prohibition against withholding workers' passports, as mandated under Kuwaiti law; punishment of forced labor cases was limited to shutting down labor recruitment firms, assessing fines, and ordering the return of withheld passports and the paying of back-wages; the government made progress in victims' protection by opening a high-capacity shelter for runaway domestic workers but still lacks formal procedures to identify and refer victims to care services (2015)