Lesotho :: Africa
Introduction
Background:
Paramount chief MOSHOESHOE I consolidated what would become Basutoland in the early 19th century and made himself king in 1822. Continuing encroachments by Dutch settlers from the neighboring Orange Free State caused the king to enter into an 1868 agreement with the UK by which Basutoland became a British protectorate, and after 1884, a crown colony. Upon independence in 1966, the country was renamed the Kingdom of Lesotho. The Basotho National Party ruled the country during its first two decades. King MOSHOESHOE II was exiled in 1990, but returned to Lesotho in 1992 and was reinstated in 1995 and subsequently succeeded by his son, King LETSIE III, in 1996. Constitutional government was restored in 1993 after seven years of military rule. In 1998, violent protests and a military mutiny following a contentious election prompted a brief but bloody intervention by South African and Botswana military forces under the aegis of the Southern African Development Community. Subsequent constitutional reforms restored relative political stability. Peaceful parliamentary elections were held in 2002, but the National Assembly elections in 2007 were hotly contested and aggrieved parties disputed how the electoral law was applied to award proportional seats in the Assembly. In 2012, competitive elections involving 18 parties saw Prime Minister Motsoahae Thomas THABANE form a coalition government - the first in the country's history - that ousted the 14-year incumbent, Pakalitha MOSISILI, who peacefully transferred power the following month. MOSISILI returned to power in snap elections in February 2015 after the collapse of THABANE's coalition government and an alleged attempted military coup. In June 2017, THABANE returned to become prime minister.
Geography
Location:
Southern Africa, an enclave of South Africa
Geographic coordinates:
29 30 S, 28 30 E
Map references:
Africa
Area:
total:
30,355 sq km
land:
30,355 sq km
water:
0 sq km
country comparison to the world: 141
Area - comparative:
slightly smaller than Maryland
Land boundaries:
total:
1,106 km
border countries (1):
South Africa 1106 km
Coastline:
0 km
(landlocked)
Maritime claims:
none (landlocked)
Climate:
temperate; cool to cold, dry winters; hot, wet summers
Terrain:
mostly highland with plateaus, hills, and mountains
Elevation:
mean elevation:
2,161 m
lowest point:
junction of the Orange and Makhaleng Rivers 1,400 m
highest point:
Thabana Ntlenyana 3,482 m
Natural resources:
water, agricultural and grazing land, diamonds, sand, clay, building stone
Land use:
agricultural land:
76.1%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
10.1%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
0.1%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent pasture:
65.9%
(2011 est.)
forest:
1.5%
(2011 est.)
other:
22.4%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
30 sq km
(2012)
Population distribution:
relatively higher population density in the western half of the nation, with the capital of Maseru, and the smaller cities of Mafeteng, Teyateyaneng, and Leribe attracting the most people as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards:
periodic droughts
Environment - current issues:
population pressure forcing settlement in marginal areas results in overgrazing, severe soil erosion, and soil exhaustion; desertification; Highlands Water Project controls, stores, and redirects water to South Africa
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
Geography - note:
landlocked, an enclave of (completely surrounded by) South Africa; mountainous, more than 80% of the country is 1,800 m above sea level
People and Society
Population:
1,969,334
(July 2020 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
country comparison to the world: 149
Nationality:
noun:
Mosotho (singular), Basotho (plural)
adjective:
Basotho
Ethnic groups:
Sotho 99.7%, Europeans, Asians, and other 0.3%
Languages:
Sesotho (official) (southern Sotho), English (official), Zulu, Xhosa
Religions:
Protestant 47.8% (Pentecostal 23.1%, Lesotho Evangelical 17.3%, Anglican 7.4%), Roman Catholic 39.3%, other Christian 9.1%, non-Christian 1.4%, none 2.3%
(2014 est.)
Demographic profile:
Lesotho faces great socioeconomic challenges. More than half of its population lives below the property line, and the country's HIV/AIDS prevalence rate is the second highest in the world. In addition, Lesotho is a small, mountainous, landlocked country with little arable land, leaving its population vulnerable to food shortages and reliant on remittances. Lesotho's persistently high infant, child, and maternal mortality rates have been increasing during the last decade, according to the last two Demographic and Health Surveys. Despite these significant shortcomings, Lesotho has made good progress in education; it is on-track to achieve universal primary education and has one of the highest adult literacy rates in Africa.
++ Lesotho's migration history is linked to its unique geography; it is surrounded by South Africa with which it shares linguistic and cultural traits. Lesotho at one time had more of its workforce employed outside its borders than any other country. Today remittances equal about 17% of its GDP. With few job options at home, a high rate of poverty, and higher wages available across the border, labor migration to South Africa replaced agriculture as the prevailing Basotho source of income decades ago. The majority of Basotho migrants were single men contracted to work as gold miners in South Africa. However, migration trends changed in the 1990s, and fewer men found mining jobs in South Africa because of declining gold prices, stricter immigration policies, and a preference for South African workers.
++ Although men still dominate cross-border labor migration, more women are working in South Africa, mostly as domestics, because they are widows or their husbands are unemployed. Internal rural-urban flows have also become more frequent, with more women migrating within the country to take up jobs in the garment industry or moving to care for loved ones with HIV/AIDS. Lesotho's small population of immigrants is increasingly composed of Taiwanese and Chinese migrants who are involved in the textile industry and small retail businesses.
Age structure:
0-14 years:
31.3%
(male 309,991/female 306,321)
15-24 years:
19.26%
(male 181,874/female 197,452)
25-54 years:
38.86%
(male 373,323/female 391,901)
55-64 years:
4.98%
(male 52,441/female 45,726)
65 years and over:
5.6%
(male 57,030/female 53,275)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
59.2
youth dependency ratio:
51.3
elderly dependency ratio:
7.9
potential support ratio:
12.7
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
24.7 years
male:
24.7 years
female:
24.7 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
Population growth rate:
0.16%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 181
Birth rate:
23.2 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
Death rate:
15.4 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
Net migration rate:
-6.1 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
Population distribution:
relatively higher population density in the western half of the nation, with the capital of Maseru, and the smaller cities of Mafeteng, Teyateyaneng, and Leribe attracting the most people as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization:
urban population:
29% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
2.83% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
202,000 MASERU (capital)
(2018)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
0.92 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
0.95 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
1.15 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
1.07 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth:
21 years
(2014 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:
544 deaths/100,000 live births
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
Infant mortality rate:
total:
41.5 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
44.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
38.1 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 37
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
53 years
male:
53.1 years
female:
53 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 226
Total fertility rate:
2.5 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 73
Contraceptive prevalence rate:
64.9%
(2018)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban:
93% of population
rural:
72.4% of population
total:
78.2% of population
unimproved:
urban:
7% of population
rural:
27.6% of population
total:
21.8% of population
(2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure:
8.8%
(2017)
Physicians density:
0.07 physicians/1,000 population
(2010)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban:
88.6% of population
rural:
52.3% of population
total:
62.4% of population
unimproved:
urban:
11.4% of population
rural:
47.7% of population
total:
37.6% of population
(2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
23.1%
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 2
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
340,000
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
4,800
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
Major infectious diseases:
degree of risk:
intermediate
(2020)
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:
16.6%
(2016)
country comparison to the world: 122
Children under the age of 5 years underweight:
10.5%
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 61
Education expenditures:
7% of GDP
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 14
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
79.4%
male:
70.1%
female:
88.3%
(2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total:
12 years
male:
12 years
female:
13 years
(2017)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total:
34.4%
male:
NA
female:
NA
(2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
Kingdom of Lesotho
conventional short form:
Lesotho
local long form:
Kingdom of Lesotho
local short form:
Lesotho
former:
Basutoland
etymology:
the name translates as "Land of the Sesotho Speakers"
Government type:
parliamentary constitutional monarchy
Capital:
name:
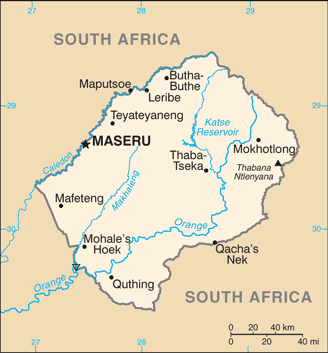
Maseru
geographic coordinates:
29 19 S, 27 29 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: in the Sesotho language the name means "[place of] red sandstones"
Administrative divisions:
10 districts; Berea, Butha-Buthe, Leribe, Mafeteng, Maseru, Mohale's Hoek, Mokhotlong, Qacha's Nek, Quthing, Thaba-Tseka
Independence:
4 October 1966 (from the UK)
National holiday:
Independence Day, 4 October (1966)
Constitution:
history:
previous 1959, 1967; latest adopted 2 April 1993 (effectively restoring the 1967 version)
amendments:
proposed by Parliament; passage of amendments affecting constitutional provisions, including fundamental rights and freedoms, sovereignty of the kingdom, the office of the king, and powers of Parliament, requires a majority vote by the National Assembly, approval by the Senate, approval in a referendum by a majority of qualified voters, and assent of the king; passage of amendments other than those specified provisions requires at least a two-thirds majority vote in both houses of Parliament; amended several times, last in 2011
Legal system:
mixed legal system of English common law and Roman-Dutch law; judicial review of legislative acts in High Court and Court of Appeal
International law organization participation:
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
yes
citizenship by descent only:
yes
dual citizenship recognized:
no
residency requirement for naturalization:
5 years
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state:
King LETSIE III (since 7 February 1996); note - King LETSIE III formerly occupied the throne from November 1990 to February 1995 while his father was in exile
head of government:
Prime Minister Moeketsi MAJORO (since 20 May 2020); note - Prime Minister Thomas THABANE resigned on 19 May 2020
cabinet:
consists of the prime minister, appointed by the King on the advice of the Council of State, the deputy prime minister, and 26 other ministers
elections/appointments:
the monarchy is hereditary, but under the terms of the constitution that came into effect after the March 1993 election, the monarch is a "living symbol of national unity" with no executive or legislative powers; under traditional law, the college of chiefs has the power to depose the monarch, to determine next in line of succession, or to serve as regent in the event that a successor is not of mature age; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition in the Assembly automatically becomes prime minister
Legislative branch:
description:
bicameral Parliament consists of: Senate (33 seats; 22 principal chiefs and 11 other senators nominated by the king with the advice of the Council of State, a 13-member body of key government and non-government officials; members serve 5-year terms) ++ National Assembly (120 seats; 80 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote and 40 elected through proportional representation; members serve 5-year terms)
elections:
Senate - last nominated by the king 11 July 2017 (next NA) ++ National Assembly - last held on 3 June 2017 (next to be held in 2022)
election results:
Senate - percent of votes by party - NA, seats by party - NA; composition - men 25, women 8, percent of women 24.2% ++ National Assembly - percent of votes by party - ABC 40.5%, DC 25.8%, LCD 9%, AD 7.3%, MEC 5.1%, BNP 4.1, PFD 2.3%, other 5.9%; seats by party - ABC 51, DC 30, LCD 11, AD 9, MEC 6, BNP 5, PFD 3, other 5; composition - men 95, women 27, percent of women 22.5%; note - total Parliament percent of women 22.9%
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Court of Appeal (consists of the court president, such number of justices of appeal as set by Parliament, and the Chief Justice and the puisne judges of the High Court ex officio); High Court (consists of the chief justice and such number of puisne judges as set by Parliament); note - both the Court of Appeal and the High Court have jurisdiction in constitutional issues
judge selection and term of office:
Court of Appeal president and High Court chief justice appointed by the monarch on the advice of the prime minister; puisne judges appointed by the monarch on advice of the Judicial Service Commission, an independent body of judicial officers and officials designated by the monarch; judges of both courts can serve until age 75
subordinate courts:
Magistrate Courts; customary or traditional courts; military courts
Political parties and leaders:
All Basotho Convention or ABC [Thomas Motsoahae THABANE] ++ Alliance of Democrats or AD [Monyane MOLELEKI] ++ Basotho Congress Party or BCP [Thulo MAHLAKENG] ++ Basotho National Party or BNP [Thesele MASERIBANE] ++ Democratic Congress or DC [Pakalitha MOSISILI] ++ Democratic Party of Lesotho or DPL [Limpho TAU] ++ Lesotho Congress for Democracy or LCD [Mothetjoa METSING] ++ Movement of Economic Change or MEC [Selibe MOCHOBOROANE] ++ National Independent Party or NIP [Kimetso MATHABA] ++ Popular Front for Democracy of PFD [Lekhetho RAKUOANE] ++ Reformed Congress of Lesotho or RCL [Keketso RANTSO]
International organization participation:
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SACU, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador Sankatana Gabriel MAJA (since 22 June 2018)
chancery:
2511 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 797-5533
FAX:
[1] (202) 234-6815
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador Rebecca E. GONZALES (since 8 February 2018)
telephone:
[266] 22 312 666
embassy:
254 Kingsway Road, Maseru West
mailing address:
P.O. Box 333, Maseru 100, Lesotho
FAX:
[266] 22 310 116
Flag description:
three horizontal stripes of blue (top), white, and green in the proportions of 3:4:3; the colors represent rain, peace, and prosperity respectively; centered in the white stripe is a black Basotho hat representing the indigenous people; the flag was unfurled in October 2006 to celebrate 40 years of independence
National symbol(s):
mokorotio (Basotho hat); national colors: blue, white, green, black
National anthem:
name:
"Lesotho fatse la bo ntat'a rona" (Lesotho, Land of Our Fathers)
lyrics/music:
Francois COILLARD/Ferdinand-Samuel LAUR
note: adopted 1967; music derives from an 1823 Swiss songbook
Economy
Economic overview:
Small, mountainous, and completely landlocked by South Africa, Lesotho depends on a narrow economic base of textile manufacturing, agriculture, remittances, and regional customs revenue. About three-fourths of the people live in rural areas and engage in animal herding and subsistence agriculture, although Lesotho produces less than 20% of the nation's demand for food. Agriculture is vulnerable to weather and climate variability.
++ Lesotho relies on South Africa for much of its economic activity; Lesotho imports 85% of the goods it consumes from South Africa, including most agricultural inputs. Households depend heavily on remittances from family members working in South Africa in mines, on farms, and as domestic workers, though mining employment has declined substantially since the 1990s. Lesotho is a member of the Southern Africa Customs Union (SACU), and revenues from SACU accounted for roughly 26% of total GDP in 2016; however, SACU revenues are volatile and expected to decline over the next 5 years. Lesotho also gains royalties from the South African Government for water transferred to South Africa from a dam and reservoir system in Lesotho. However, the government continues to strengthen its tax system to reduce dependency on customs duties and other transfers.
++ The government maintains a large presence in the economy - government consumption accounted for about 26% of GDP in 2017. The government remains Lesotho's largest employer; in 2016, the government wage bill rose to 23% of GDP – the largest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Lesotho's largest private employer is the textile and garment industry - approximately 36,000 Basotho, mainly women, work in factories producing garments for export to South Africa and the US. Diamond mining in Lesotho has grown in recent years and accounted for nearly 35% of total exports in 2015. Lesotho managed steady GDP growth at an average of 4.5% from 2010 to 2014, dropping to about 2.5% in 2015-16, but poverty remains widespread around 57% of the total population.
GDP real growth rate:
-1.6%
(2017 est.)
3.1%
(2016 est.)
2.5%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
5.3%
(2019 est.)
3.8%
(2018 est.)
5.1%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
Credit ratings:
Fitch rating:
B
(2019)
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$5.623 billion
(2019 est.)
$5.539 billion
(2018 est.)
$5.564 billion
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$2.462 billion
(2019 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$1,384
(2019 est.)
$1,375
(2018 est.)
$1,392
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
country comparison to the world: 203
Gross national saving:
20.3% of GDP
(2017 est.)
19.7% of GDP
(2016 est.)
24.7% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
5.8%
(2016 est.)
industry:
39.2%
(2016 est.)
services:
54.9%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
69.2%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
26.4%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
31.4%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
-13.4%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
40.8%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-54.4%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
88.2
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
corn, wheat, pulses, sorghum, barley; livestock
Industries:
food, beverages, textiles, apparel assembly, handicrafts, construction, tourism
Industrial production growth rate:
12.5%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
Labor force:
930,800
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
86%
industry and services:
14%
(2002 est.)
note: most of the resident population is engaged in subsistence agriculture; roughly 35% of the active male wage earners work in South Africa
Unemployment rate:
28.1%
(2014 est.)
25%
(2008 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
Population below poverty line:
57%
(2016 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
1%
highest 10%:
39.4%
(2003)
Budget:
revenues:
1.09 billion
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
1.255 billion
(2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
39.7% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-6% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
Public debt:
33.7% of GDP
(2017 est.)
36.2% of GDP
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 155
Fiscal year:
1 April - 31 March
Current account balance:
-$102 million
(2017 est.)
-$201 million
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
Exports:
$1.106 billion
(2019 est.)
$1.271 billion
(2018 est.)
$1.145 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
Exports - partners:
South Africa 57%, US 33.5%
(2017)
Exports - commodities:
manufactures (clothing, footwear), wool and mohair, food and live animals, electricity, water, diamonds
Imports:
$2.613 billion
(2019 est.)
$2.707 billion
(2018 est.)
$2.688 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
Imports - commodities:
food; building materials, vehicles, machinery, medicines, petroleum products
Imports - partners:
South Africa 87.2%
(2017)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$657.7 million
(31 December 2017 est.)
$925.2 million
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
Debt - external:
$934.6 million
(31 December 2017 est.)
$921.3 million
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
Exchange rates:
maloti (LSL) per US dollar -
14.48
(2017 est.)
14.71
(2016 est.)
14.71
(2015 est.)
12.76
(2014 est.)
10.85
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access:
population without electricity:
1 million
(2019)
electrification - total population:
36%
(2019)
electrification - urban areas:
63%
(2019)
electrification - rural areas:
26%
(2019)
Electricity - production:
510 million kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
Electricity - consumption:
847.3 million kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
Electricity - exports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
Electricity - imports:
373 million kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
80,400 kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 127
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
100% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 1
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
1% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
Crude oil - production:
0 bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 162
Crude oil - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
Crude oil - imports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
Crude oil - proved reserves:
0 bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
Refined petroleum products - production:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 165
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
5,000 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
Refined petroleum products - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
Refined petroleum products - imports:
5,118 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
Natural gas - production:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
Natural gas - consumption:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 167
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
Natural gas - imports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
Natural gas - proved reserves:
0 cu m
(1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
711,100 Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
7,865
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 194
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
2,238,186
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
113.83
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
mobile penetration remains below regional average; introduction of mobile broadband in the country & LTE technology, with 5G trials in early 2019; fixed-line teledensity is low; mobile-cellular telephone system is growth sector; regulator considering improving SIM card registration
(2020)
domestic:
fixed-line is 1 per 100 subscriptions; mobile-cellular service dominates the market with a subscribership now over 114 per 100 persons; rudimentary system consisting of a modest number of landlines, a small microwave radio relay system, and a small radiotelephone communication system
(2019)
international:
country code - 266; Internet accessibility has improved with several submarine fiber optic cables that land on African east and west coasts, but the country's land locked position makes access prices expensive; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean)
(2019)
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
1 state-owned TV station and 2 state-owned radio stations; government controls most private broadcast media; satellite TV subscription service available; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters obtainable
(2019)
Internet country code:
.ls
Internet users:
total:
569,114
percent of population:
29%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
5,763
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
Transportation
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
7P
(2016)
Airports:
24
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 130
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
3
(2019)
over 3,047 m:
1
914 to 1,523 m:
1
under 914 m:
1
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
21
(2013)
914 to 1,523 m:
5
(2013)
under 914 m:
16
(2013)
Roadways:
total:
5,940 km
(2011)
paved:
1,069 km
(2011)
unpaved:
4,871 km
(2011)
country comparison to the world: 144
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Lesotho Defense Force (LDF): Army (includes Air Wing)
(2019)
Military expenditures:
1.5% of GDP
(2019)
1.8% of GDP
(2018)
2% of GDP
(2017)
1.8% of GDP
(2016)
1.9% of GDP
(2015)
country comparison to the world: 82
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Lesotho Defense Force (LDF) has approximately 2,000 personnel, including 150 for its air wing
(2019 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
the LDF's inventory consists of older equipment from a variety of countries; the only reported delivery to the LDF since 2007 was two helicopters from France in 2017
(2019 est.)
Military service age and obligation:
18-24 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; women serve as commissioned officers
(2019)
Military - note:
Lesotho's declared policy for its military is the maintenance of the country's sovereignty and the preservation of internal security; in practice, external security is guaranteed by South Africa
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
South Africa has placed military units to assist police operations along the border of Lesotho, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique to control smuggling, poaching, and illegal migration
Trafficking in persons:
current situation:
Lesotho is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking and for men subjected to forced labor; in Lesotho and South Africa, Basotho women and children are subjected to domestic servitude, and Basotho children increasingly endure commercial sexual exploitation; some Basotho men who voluntarily migrate to South Africa for work become victims of forced labor in agriculture and mining or are coerced into committing crimes; foreign nationals continue to traffic fellow citizens in Lesotho
tier rating:
Tier 2 Watch List – Lesotho does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; in 2014, Lesotho was granted a waiver from an otherwise required downgrade to Tier 3 because its government has a written plan that, if implemented would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; the government failed to initiate any prosecutions against alleged traffickers and has not convicted any offenders under the 2011 anti-trafficking act, which remains unimplemented for a fifth year; authorities did not develop formal victim identification and referral procedures, did not establish victim care centers, as required under the 2011 anti-trafficking act, and did not support NGOs offering victims protective services (2015)