Togo :: Africa
Introduction
Background:
From the 11th to the 16th centuries, various ethnic groups settled the Togo region. From the 16th to the 18th centuries, the coastal region became a major slave trading center and the surrounding region took on the name of "The Slave Coast." In 1884, Germany declared a region including present-day Togo as a protectorate called Togoland. After World War I, rule over Togo was transferred to France. French Togoland became Togo upon independence in 1960. Gen. Gnassingbe EYADEMA, installed as military ruler in 1967, ruled Togo with a heavy hand for almost four decades. Despite the facade of multi-party elections instituted in the early 1990s, the government was largely dominated by President EYADEMA, whose Rally of the Togolese People (RPT) party has been in power almost continually since 1967 and its successor, the Union for the Republic, maintains a majority of seats in today's legislature. Upon EYADEMA's death in February 2005, the military installed the president's son, Faure GNASSINGBE, and then engineered his formal election two months later. Democratic gains since then allowed Togo to hold its first relatively free and fair legislative elections in October 2007. Since 2007, President GNASSINGBE has started the country along a gradual path to democratic reform. Togo has since held multiple presidential and legislative elections deemed generally free and fair by international observers. Despite those positive moves, political reconciliation has moved slowly, and the country experiences periodic outbursts of violent protest by frustrated citizens. Recent constitutional changes to institute a runoff system in presidential elections and establish term limits has done little to reduce the resentment many Togolese feel after over 50 years of one-family rule.
Geography
Location:
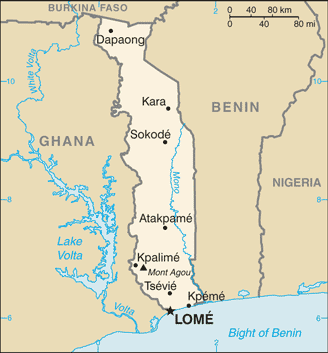
Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Benin, between Benin and Ghana
Geographic coordinates:
8 00 N, 1 10 E
Map references:
Africa
Area:
total:
56,785 sq km
land:
54,385 sq km
water:
2,400 sq km
country comparison to the world: 126
Area - comparative:
slightly smaller than West Virginia
Land boundaries:
total:
1,880 km
border countries (3):
Benin 651 km, Burkina Faso 131 km, Ghana 1098 km
Coastline:
56 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea:
30
nm
exclusive economic zone:
200
nm
Climate:
tropical; hot, humid in south; semiarid in north
Terrain:
gently rolling savanna in north; central hills; southern plateau; low coastal plain with extensive lagoons and marshes
Elevation:
mean elevation:
236 m
lowest point:
Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point:
Mont Agou 986 m
Natural resources:
phosphates, limestone, marble, arable land
Land use:
agricultural land:
67.4%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
45.2%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
3.8%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent pasture:
18.4%
(2011 est.)
forest:
4.9%
(2011 est.)
other:
27.7%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
70 sq km
(2012)
Population distribution:
one of the more densely populated African nations with most of the population residing in rural communities, density is highest in the south on or near the Atlantic coast as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards:
hot, dry harmattan wind can reduce visibility in north during winter; periodic droughts
Environment - current issues:
deforestation attributable to slash-and-burn agriculture and the use of wood for fuel; very little rain forest still present and what remains is highly degraded; desertification; water pollution presents health hazards and hinders the fishing industry; air pollution increasing in urban areas
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
Geography - note:
the country's length allows it to stretch through six distinct geographic regions; climate varies from tropical to savanna
People and Society
Population:
8,608,444
(July 2020 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
country comparison to the world: 99
Nationality:
noun:
Togolese (singular and plural)
adjective:
Togolese
Ethnic groups:
Adja-Ewe/Mina 42.4%, Kabye/Tem 25.9%, Para-Gourma/Akan 17.1%, Akposso/Akebu 4.1%, Ana-Ife 3.2%, other Togolese 1.7%, foreigners 5.2%, no response .4%
(2013-14 est.)
note: Togo has an estimated 37 ethnic groups
Languages:
French (official, the language of commerce), Ewe and Mina (the two major African languages in the south), Kabye (sometimes spelled Kabiye) and Dagomba (the two major African languages in the north)
Religions:
Christian 43.7%, folk 35.6%, Muslim 14%, Hindu <.1%, Buddhist <.1%, Jewish <.1%, other .5%, none 6.2%
(2010 est.)
Demographic profile:
Togo's population is estimated to have grown to four times its size between 1960 and 2010. With nearly 60% of its populace under the age of 25 and a high annual growth rate attributed largely to high fertility, Togo's population is likely to continue to expand for the foreseeable future. Reducing fertility, boosting job creation, and improving education will be essential to reducing the country's high poverty rate. In 2008, Togo eliminated primary school enrollment fees, leading to higher enrollment but increased pressure on limited classroom space, teachers, and materials. Togo has a good chance of achieving universal primary education, but educational quality, the underrepresentation of girls, and the low rate of enrollment in secondary and tertiary schools remain concerns.
++ Togo is both a country of emigration and asylum. In the early 1990s, southern Togo suffered from the economic decline of the phosphate sector and ethnic and political repression at the hands of dictator Gnassingbe EYADEMA and his northern, Kabye-dominated administration. The turmoil led 300,000 to 350,000 predominantly southern Togolese to flee to Benin and Ghana, with most not returning home until relative stability was restored in 1997. In 2005, another outflow of 40,000 Togolese to Benin and Ghana occurred when violence broke out between the opposition and security forces over the disputed election of EYADEMA's son Faure GNASSINGBE to the presidency. About half of the refugees reluctantly returned home in 2006, many still fearing for their safety. Despite ethnic tensions and periods of political unrest, Togo in September 2017 was home to more than 9,600 refugees from Ghana.
Age structure:
0-14 years:
39.73%
(male 1,716,667/female 1,703,230)
15-24 years:
19.03%
(male 817,093/female 820,971)
25-54 years:
33.26%
(male 1,423,554/female 1,439,380)
55-64 years:
4.42%
(male 179,779/female 200,392)
65 years and over:
3.57%
(male 132,304/female 175,074)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
77.1
youth dependency ratio:
72
elderly dependency ratio:
5.1
potential support ratio:
19.4
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
20 years
male:
19.7 years
female:
20.3 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
Population growth rate:
2.56%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Birth rate:
32 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
Death rate:
6.5 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
Net migration rate:
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
Population distribution:
one of the more densely populated African nations with most of the population residing in rural communities, density is highest in the south on or near the Atlantic coast as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization:
urban population:
42.8% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
3.76% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
1.828 million LOME (capital)
(2020)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
1 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.76 male(s)/female
total population:
0.98 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth:
21 years
(2013/14 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:
396 deaths/100,000 live births
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
Infant mortality rate:
total:
38.5 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
44.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
32.3 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
66.6 years
male:
63.9 years
female:
69.3 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
Total fertility rate:
4.22 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
Contraceptive prevalence rate:
23.9%
(2017)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban:
92.3% of population
rural:
56% of population
total:
70.9% of population
unimproved:
urban:
7.7% of population
rural:
44% of population
total:
29.1% of population
(2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure:
6.2%
(2017)
Physicians density:
0.03 physicians/1,000 population
(2017)
Hospital bed density:
0.7 beds/1,000 population
(2011)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban:
80.4% of population
(2015 est.)
rural:
16.2% of population
total:
41.6% of population
unimproved:
urban:
19.6% of population
rural:
83.8% of population
total:
57.4% of population
(2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
2.3%
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
120,000
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 41
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
3,000
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
Major infectious diseases:
degree of risk:
very high
(2020)
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria, dengue fever, and yellow fever
water contact diseases:
schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases:
rabies
respiratory diseases:
meningococcal meningitis
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:
8.4%
(2016)
country comparison to the world: 152
Children under the age of 5 years underweight:
15.2%
(2017)
country comparison to the world: 39
Education expenditures:
5.4% of GDP
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 41
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
63.7%
male:
77.3%
female:
51.2%
(2015)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total:
13 years
male:
14 years
NA
female:
12 years
NA
(2017)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total:
3.9%
male:
3.7%
female:
4.1%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 168
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
Togolese Republic
conventional short form:
Togo
local long form:
Republique Togolaise
local short form:
none
former:
French Togoland
etymology:
derived from the Ewe words "to" (river) and "godo" (on the other side) to give the sense of "on the other side of the river"; originally, this designation applied to the town of Togodo (now Togoville) on the northern shore of Lake Togo, but the name was eventually extended to the entire nation
Government type:
presidential republic
Capital:
name:
Lome
geographic coordinates:
6 07 N, 1 13 E
time difference:
UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: Lome comes from "alotime" which in the native Ewe language means "among the alo plants"; alo trees dominated the city's original founding site
Administrative divisions:
5 regions (regions, singular - region); Centrale, Kara, Maritime, Plateaux, Savanes
Independence:
27 April 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship)
National holiday:
Independence Day, 27 April (1960)
Constitution:
history:
several previous; latest adopted 27 September 1992, effective 14 October 1992
amendments:
proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one fifth of the National Assembly membership; passage requires four-fifths majority vote by the Assembly; a referendum is required if approved by only two-thirds majority of the Assembly or if requested by the president; constitutional articles on the republican and secular form of government cannot be amended; amended 2002, 2007, 2019 when the National Assembly unanimously approved a package of amendments, including setting presidential term limits of two 5-year mandates
Legal system:
customary law system
International law organization participation:
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
no
citizenship by descent only:
at least one parent must be a citizen of Togo
dual citizenship recognized:
yes
residency requirement for naturalization:
5 years
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state:
President Faure GNASSINGBE (since 4 May 2005)
head of government:
Prime Minister Victoire Tomegah DOGBE (since 28 September 2020)
cabinet:
Council of Ministers appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister
elections/appointments:
president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 5-year term (no term limits); election last held on 22 February 2020 (next to be held February 2025); prime minister appointed by the president
election results:
Faure GNASSINGBE reelected president; percent of vote - Faure GNASSINGBE (UNIR) 72.4%, Agbeyome KODJO (MPDD) 18.4%, Jean-Pierre FABRE (ANC) 4.4%, other 5%
Legislative branch:
description:
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (91 seats; members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by closed, party-list proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)
elections:
last held on 20 December 2018 (next to be held in 2023)
election results:
percent of vote by coalition/party - NA; seats by party - UNIR 59, UFC 6, NET 3, MPDD 3, other 2, independent 18; composition - men 75, women 16, percent of women 17.6%
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (organized into criminal and administrative chambers, each with a chamber president and advisors); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 judges, including the court president)
judge selection and term of office:
Supreme Court president appointed by decree of the president of the republic upon the proposal of the Supreme Council of the Magistracy, a 9-member judicial, advisory, and disciplinary body; other judicial appointments and judge tenure NA; Constitutional Court judges appointed by the National Assembly; judge tenure NA
subordinate courts:
Court of Assizes (sessions court); Appeal Court; tribunals of first instance (divided into civil, commercial, and correctional chambers; Court of State Security; military tribunal
Political parties and leaders:
Action Committee for Renewal or CAR [Yaovi AGBOYIBO] ++ Alliance of Democrats for Integral Development or ADDI [Tchaboure GOGUE] ++ Democratic Convention of African Peoples or CDPA [Brigitte ADJAMAGBO-JOHNSON] ++ Democratic Forces for the Republic or FDR [Dodji APEVON] ++ National Alliance for Change or ANC [Jean-Pierre FABRE] ++ New Togolese Commitment [Gerry TAAMA] ++ Pan-African National Party or PNP [Tikpi ATCHADAM] ++ Pan-African Patriotic Convergence or CPP [Edem KODJO] ++ Patriotic Movement for Democracy and Development or MPDD [Agbeyome KODJO] ++ Socialist Pact for Renewal or PSR [Abi TCHESSA] ++ The Togolese Party [Nathaniel OLYMPIO] ++ Union of Forces for Change or UFC [Gilchrist OLYMPIO] ++ Union for the Republic or UNIR [Faure GNASSINGBE]
International organization participation:
ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, EITI (compliant country), Entente, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WADB (regional), WAEMU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador Frederic Edem HEGBE (since 24 April 2017)
chancery:
2208 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 234-4212
FAX:
[1] (202) 232-3190
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador Eric W. STROHMAYER (since 11 April 2019)
telephone:
[228] 2261-5470
embassy:
4332 Blvd. Eyadema, Lome
mailing address:
B.P. 852, Lome; 2300 Lome Place, Washington, DC 20521-2300
FAX:
[228] 2261-5501
Flag description:
five equal horizontal bands of green (top and bottom) alternating with yellow; a white five-pointed star on a red square is in the upper hoist-side corner; the five horizontal stripes stand for the five different regions of the country; the red square is meant to express the loyalty and patriotism of the people, green symbolizes hope, fertility, and agriculture, while yellow represents mineral wealth and faith that hard work and strength will bring prosperity; the star symbolizes life, purity, peace, dignity, and Togo's independence
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
National symbol(s):
lion; national colors: green, yellow, red, white
National anthem:
name:
"Salut a toi, pays de nos aieux" (Hail to Thee, Land of Our Forefathers)
lyrics/music:
Alex CASIMIR-DOSSEH
note: adopted 1960, restored 1992; this anthem was replaced by another during one-party rule between 1979 and 1992
Economy
Economic overview:
Togo has enjoyed a period of steady economic growth fueled by political stability and a concerted effort by the government to modernize the country's commercial infrastructure, but discontent with President Faure GNASSINGBE has led to a rapid rise in protests, creating downside risks. The country completed an ambitious large-scale infrastructure improvement program, including new principal roads, a new airport terminal, and a new seaport. The economy depends heavily on both commercial and subsistence agriculture, providing employment for around 60% of the labor force. Some basic foodstuffs must still be imported. Cocoa, coffee, and cotton and other agricultural products generate about 20% of export earnings with cotton being the most important cash crop. Togo is among the world's largest producers of phosphate and seeks to develop its carbonate phosphate reserves, which provide more than 20% of export earnings.
++ Supported by the World Bank and the IMF, the government's decade-long effort to implement economic reform measures, encourage foreign investment, and bring revenues in line with expenditures has moved slowly. Togo completed its IMF Extended Credit Facility in 2011 and reached a Heavily Indebted Poor Country debt relief completion point in 2010 at which 95% of the country's debt was forgiven. Togo continues to work with the IMF on structural reforms, and in January 2017, the IMF signed an Extended Credit Facility arrangement consisting of a three-year $238 million loan package. Progress depends on follow through on privatization, increased transparency in government financial operations, progress toward legislative elections, and continued support from foreign donors.
++ Togo's 2017 economic growth probably remained steady at 5.0%, largely driven by infusions of foreign aid, infrastructure investment in its port and mineral industry, and improvements in the business climate. Foreign direct investment inflows have slowed in recent years.
GDP real growth rate:
4.4%
(2017 est.)
5.1%
(2016 est.)
5.7%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
0.6%
(2019 est.)
0.9%
(2018 est.)
-0.9%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
Credit ratings:
Moody's rating:
B3
(2019)
Standard & Poors rating:
B
(2019)
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$11.38 billion
(2018 est.)
$12.97 billion
(2017 est.)
$10.85 billion
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$5.232 billion
(2018 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$672
(2018 est.)
$1,700
(2017 est.)
$657
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 218
Gross national saving:
16.1% of GDP
(2017 est.)
21.8% of GDP
(2016 est.)
21.2% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
28.8%
(2017 est.)
industry:
21.8%
(2017 est.)
services:
49.8%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
84.5%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
11.4%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
23.4%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
-1.4%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
43.1%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-61%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
63.7
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
coffee, cocoa, cotton, yams, cassava (manioc, tapioca), corn, beans, rice, millet, sorghum; livestock; fish
Industries:
phosphate mining, agricultural processing, cement, handicrafts, textiles, beverages
Industrial production growth rate:
5%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
Labor force:
2.595 million
(2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
65%
industry:
5%
services:
30%
(1998 est.)
Unemployment rate:
6.9%
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
Population below poverty line:
55.1%
(2015 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
3.3%
highest 10%:
27.1%
(2006)
Budget:
revenues:
1.023 billion
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
1.203 billion
(2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
21.5% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-3.8% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 154
Public debt:
75.7% of GDP
(2017 est.)
81.6% of GDP
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 40
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Current account balance:
-$383 million
(2017 est.)
-$416 million
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
Exports:
$1.862 billion
(2018 est.)
$1.881 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
Exports - partners:
Benin 16.7%, Burkina Faso 15.2%, Niger 8.9%, India 7.3%, Mali 6.7%, Ghana 5.5%, Cote dIvoire 5.4%, Nigeria 4.1%
(2017)
Exports - commodities:
reexports, cotton, phosphates, coffee, cocoa
Imports:
$2.911 billion
(2018 est.)
$2.789 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
Imports - commodities:
machinery and equipment, foodstuffs, petroleum products
Imports - partners:
China 27.5%, France 9.1%, Netherlands 4.4%, Japan 4.3%
(2017)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$77.8 million
(31 December 2017 est.)
$42.6 million
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
Debt - external:
$1.442 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$1.22 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 160
Exchange rates:
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) per US dollar -
617.4
(2017 est.)
593.01
(2016 est.)
593.01
(2015 est.)
591.45
(2014 est.)
494.42
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access:
population without electricity:
5 million
(2019)
electrification - total population:
43%
(2019)
electrification - urban areas:
77%
(2019)
electrification - rural areas:
19%
(2019)
Electricity - production:
232.6 million kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
Electricity - consumption:
1.261 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
Electricity - exports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Electricity - imports:
1.14 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
230,000 kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 164
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
70% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
29% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 71
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
1% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
Crude oil - production:
0 bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 207
Crude oil - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
Crude oil - imports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
Crude oil - proved reserves:
0 bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
Refined petroleum products - production:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
15,000 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 152
Refined petroleum products - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
Refined petroleum products - imports:
13,100 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
Natural gas - production:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
Natural gas - consumption:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
Natural gas - imports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
Natural gas - proved reserves:
0 cu m
(1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 200
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
2.651 million Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 151
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
45,311
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
6,477,816
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
77.2
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
system based on a network of microwave radio relay routes supplemented by open-wire lines and a mobile-cellular system; telecoms supply 8% of GDP; 3 mobile operators; 12% of residents have access to the Internet; mobile subscribers and mobile broadband both increasing
(2020)
domestic:
fixed-line less than 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular 77 telephones per 100 persons with mobile-cellular use predominating
(2019)
international:
country code - 228; landing point for the WACS submarine cable, linking countries along the west coast of Africa with each other and with Portugal; satellite earth stations - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean), 1 Symphonie
(2020)
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
1 state-owned TV station with multiple transmission sites; five private TV stations broadcast locally; cable TV service is available; state-owned radio network with two stations (in Lome and Kara); several dozen private radio stations and a few community radio stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters available
(2019)
Internet country code:
.tg
Internet users:
total:
1,010,609
percent of population:
12.36%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 141
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
26,156
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 146
Transportation
National air transport system:
number of registered air carriers:
1
(2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers:
8
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers:
566,295
(2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers:
10.89 million
mt-km
(2018)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
5V
(2016)
Airports:
8
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 163
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
2
(2019)
2,438 to 3,047 m:
2
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
6
(2013)
914 to 1,523 m:
4
(2013)
under 914 m:
2
(2013)
Pipelines:
62 km gas
Railways:
total:
568 km
(2014)
narrow gauge:
568 km
1.000-m gauge
(2014)
country comparison to the world: 111
Roadways:
total:
11,734 km
(2081)
paved:
1,794 km
(2018)
unpaved:
8,157 km
(2018)
urban:
1,783 km
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 133
Waterways:
50 km
(seasonally navigable by small craft on the Mono River depending on rainfall)
(2011)
country comparison to the world: 102
Merchant marine:
total:
405
by type:
bulk carrier 5, container ship 5, general cargo 266, oil tanker 50, other 79
(2019)
country comparison to the world: 44
Ports and terminals:
major seaport(s):
Kpeme, Lome
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Togolese Armed Forces (Forces Armees Togolaise, FAT): Togolese Army (l'Armee de Terre), Togolese Navy (Forces Naval Togolaises), Togolese Air Force (Armee de l'Air), National Gendarmerie
(2020)
Military expenditures:
3.1% of GDP
(2019)
2% of GDP
(2018)
1.9% of GDP
(2017)
1.9% of GDP
(2016)
1.7% of GDP
(2015)
country comparison to the world: 26
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Togolese Armed Forces (FAT) are comprised of approximately 9,100 personnel (8,000 Army; 200 Navy; 200 Navy; 750 Gendarmerie)
(2019 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
the FAT's small inventory is a mix of older Brazilian, British, French, German, Russian/Soviet, and US equipment; since 2010, France is the leading supplier of military hardware to Togo
(2020)
Military deployments:
920 Mali (MINUSMA)
(2020)
Military service age and obligation:
18 years of age for military service; 2-year service obligation; currently the military is only an all-volunteer force
(2017)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
in 2001, Benin claimed Togo moved boundary monuments - joint commission continues to resurvey the boundary; talks continue between Benin and Togo on funding the Adjrala hydroelectric dam on the Mona River
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
refugees (country of origin):
9,556 (Ghana) (2020)
Illicit drugs:
transit hub for Nigerian heroin and cocaine traffickers; money laundering not a significant problem