Taiwan :: East & Southeast Asia
Introduction
Background:
First inhabited by Austronesian people, Taiwan became home to Han immigrants beginning in the late Ming Dynasty (17th century). In 1895, military defeat forced China's Qing Dynasty to cede Taiwan to Japan, which then governed Taiwan for 50 years. Taiwan came under Chinese Nationalist (Kuomintang, KMT) control after World War II. With the communist victory in the Chinese civil war in 1949, the Nationalist-controlled Republic of China government and 2 million Nationalists fled to Taiwan and continued to claim to be the legitimate government for mainland China and Taiwan based on a 1947 Constitution drawn up for all of China. Until 1987, however, the Nationalist government ruled Taiwan under a civil war martial law declaration dating to 1948. Beginning in the 1970s, Nationalist authorities gradually began to incorporate the native population into the governing structure beyond the local level. The democratization process expanded rapidly in the 1980s, leading to the then illegal founding of Taiwan's first opposition party (the Democratic Progressive Party or DPP) in 1986 and the lifting of martial law the following year. Taiwan held legislative elections in 1992, the first in over forty years, and its first direct presidential election in 1996. In the 2000 presidential elections, Taiwan underwent its first peaceful transfer of power with the KMT loss to the DPP and afterwards experienced two additional democratic transfers of power in 2008 and 2016. Throughout this period, the island prospered, became one of East Asia's economic "Tigers," and after 2000 became a major investor in mainland China as cross-Strait ties matured. The dominant political issues continue to be economic reform and growth as well as management of sensitive relations between Taiwan and China.
Geography
Location:
Eastern Asia, islands bordering the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, South China Sea, and Taiwan Strait, north of the Philippines, off the southeastern coast of China
Geographic coordinates:
23 30 N, 121 00 E
Map references:
Southeast Asia
Area:
total:
35,980 sq km
land:
32,260 sq km
water:
3,720 sq km
note: includes the Pescadores, Matsu, and Quemoy islands
country comparison to the world: 138
Area - comparative:
slightly smaller than Maryland and Delaware combined
Land boundaries:
0 km
Coastline:
1,566.3 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea:
12
nm
exclusive economic zone:
200
nm
Climate:
tropical; marine; rainy season during southwest monsoon (June to August); persistent and extensive cloudiness all year
Terrain:
eastern two-thirds mostly rugged mountains; flat to gently rolling plains in west
Elevation:
mean elevation:
1,150 m
lowest point:
South China Sea 0 m
highest point:
Yu Shan 3,952 m
Natural resources:
small deposits of coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, asbestos, arable land
Land use:
agricultural land:
22.7%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
16.9%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
5.8%
(2011 est.)
other:
77.3%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
3,820 sq km
(2012)
Population distribution:
distribution exhibits a peripheral coastal settlement pattern, with the largest populations on the north and west coasts
Natural hazards:
earthquakes; typhoons
++ volcanism: Kueishantao Island (401 m), east of Taiwan, is its only historically active volcano, although it has not erupted in centuries
Environment - current issues:
air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water supplies; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan's international status
Geography - note:
strategic location adjacent to both the Taiwan Strait and the Luzon Strait
People and Society
Population:
23,603,049
(July 2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
Nationality:
noun:
Taiwan (singular and plural)
adjective:
Taiwan (or Taiwanese)
note: example - he or she is from Taiwan; they are from Taiwan
Ethnic groups:
Han Chinese (including Hoklo, who compose approximately 70% of Taiwan's population, Hakka, and other groups originating in mainland China) more than 95%, indigenous Malayo-Polynesian peoples 2.3%
note 1: there are 16 officially recognized indigenous groups: Amis, Atayal, Bunun, Hla'alua, Kanakaravu, Kavalan, Paiwan, Puyuma, Rukai, Saisiyat, Sakizaya, Seediq, Thao, Truku, Tsou, and Yami; Amis, Paiwan, and Atayal are the largest and account for roughly 70% of the indigenous population ++ note 2: although not definitive, the majority of current genetic, archeological, and linguistic data support the theory that Taiwan is the ultimate source for the spread of humans across the Pacific to Polynesia; the expansion (ca. 3000 B.C. to A.D. 1200) took place via the Philippines and eastern Indonesia and reached Fiji and Tonga by about 900 B.C.; from there voyagers spread across all of the rest of the Pacific islands over the next two millennia
Languages:
Mandarin Chinese (official), Taiwanese (Min Nan), Hakka dialects, approximately 16 indigenous languages
Religions:
Buddhist 35.3%, Taoist 33.2%, Christian 3.9%, folk (includes Confucian) approximately 10%, none or unspecified 18.2%
(2005 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years:
12.42%
(male 1,504,704/female 1,426,494)
15-24 years:
11.62%
(male 1,403,117/female 1,339,535)
25-54 years:
45.51%
(male 5,351,951/female 5,389,112)
55-64 years:
14.73%
(male 1,698,555/female 1,778,529)
65 years and over:
15.72%
(male 1,681,476/female 2,029,576)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
40
youth dependency ratio:
17.8
elderly dependency ratio:
22.2
potential support ratio:
4.5
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
42.3 years
male:
41.5 years
female:
43.1 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 36
Population growth rate:
0.11%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 186
Birth rate:
8 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 222
Death rate:
7.9 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
Net migration rate:
0.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
Population distribution:
distribution exhibits a peripheral coastal settlement pattern, with the largest populations on the north and west coasts
Urbanization:
urban population:
78.9% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
0.8% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
4.398 million New Taipei City, 2.721 million TAIPEI (capital), 2.245 million Taoyuan, 1.538 million Kaohsiung, 1.321 million Taichung, 850,000 Tainan
(2020)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.06 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
1.05 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
0.99 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.83 male(s)/female
total population:
0.97 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
total:
4.2 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
4.6 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
3.8 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
80.6 years
male:
77.5 years
female:
83.9 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
Total fertility rate:
1.14 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 225
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
NA
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
NA
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
NA
Education expenditures:
NA
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write
total population:
98.5%
male:
99.7%
female:
97.3%
(2014)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
none
conventional short form:
Taiwan
local long form:
none
local short form:
Taiwan
former:
Formosa
etymology:
"Tayowan" was the name of the coastal sandbank where the Dutch erected their colonial headquarters on the island in the 17th century; the former name "Formosa" means "beautiful" in Portuguese
Government type:
semi-presidential republic
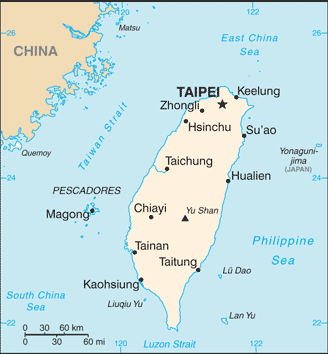
Capital:
name:
Taipei
geographic coordinates:
25 02 N, 121 31 E
time difference:
UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the Chinese meaning is "Northern Taiwan," reflecting the city's position in the far north of the island
Administrative divisions:
includes main island of Taiwan plus smaller islands nearby and off coast of China's Fujian Province; Taiwan is divided into 13 counties (xian, singular and plural), 3 cities (shi, singular and plural), and 6 special municipalities directly under the jurisdiction of the Executive Yuan
++ counties: Changhua, Chiayi, Hsinchu, Hualien, Kinmen, Lienchiang, Miaoli, Nantou, Penghu, Pingtung, Taitung, Yilan, Yunlin
++ cities: Chiayi, Hsinchu, Keelung
++ special municipalities: Kaohsiung (city), New Taipei (city), Taichung (city), Tainan (city), Taipei (city), Taoyuan (city)
note: Taiwan uses a variety of romanization systems; while a modified Wade-Giles system still dominates, the city of Taipei has adopted a Pinyin romanization for street and place names within its boundaries; other local authorities use different romanization systems
National holiday:
Republic Day (National Day), 10 October (1911); note - celebrates the anniversary of the Chinese Revolution, also known as Double Ten (10-10) Day
Constitution:
history:
previous 1912, 1931; latest adopted 25 December 1946, promulgated 1 January 1947, effective 25 December 1947
amendments:
proposed by at least one fourth of the Legislative Yuan membership; passage requires approval by at least three-fourths majority vote of at least three fourths of the Legislative Yuan membership and approval in a referendum by more than half of eligible voters; revised several times, last in 2005
Legal system:
civil law system
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
no
citizenship by descent only:
at least one parent must be a citizen of Taiwan
dual citizenship recognized:
yes, except that citizens of Taiwan are not recognized as dual citizens of the People's Republic of China
residency requirement for naturalization:
5 years
Suffrage:
20 years of age; universal; note - in mid-2016, the Legislative Yuan drafted a constitutional amendment to reduce the voting age to 18, but it has not passed as of December 2017
Executive branch:
chief of state:
President TSAI Ing-wen (since 20 May 2016; re-elected on 11 Jan 2020); Vice President CHEN Chien-jen (since 20 May 2016)
head of government:
Premier SU Tseng-chang (President of the Executive Yuan) (since 11 January 2019); Vice Premier SHIH Jun-ji, Vice President of the Executive Yuan (since 8 September 2017)
cabinet:
Executive Yuan - ministers appointed by president on recommendation of premier
elections/appointments:
president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by simple majority popular vote for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 11 January 2020 (next to be held on 11 January 2024); premier appointed by the president; vice premiers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the premier
election results:
TSAI Ing-wen elected president; percent of vote - TSAI Ing-wen (DPP) 57.1%, HAN Kuo-yu (KMT) 38.6%; note - TSAI is the first woman elected president of Taiwan
Legislative branch:
description:
unicameral Legislative Yuan (113 seats; 73 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote, 34 directly elected in a single island-wide constituency by proportional representation vote, and 6 directly elected in multi-seat aboriginal constituencies by proportional representation vote; members serve 4-year terms)
elections:
last held on 11 January 2020 (next to be held on 11 January 2024)
election results:
percent of vote by party - Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) 34.0%, Kuomintang (KMT) 33.4%, Taiwan People's Party (TPP) 11.2%; seats by party - DPP 61, KMT 38, TPP 5
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Supreme Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and approximately 100 judges organized into 8 civil and 12 criminal divisions, each with a division chief justice and 4 associate justices); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 13 justices)
judge selection and term of office:
Supreme Court justices appointed by the president; Constitutional Court justices appointed by the president, with approval of the Legislative Yuan; Supreme Court justices serve for life; Constitutional Court justices appointed for 8-year terms, with half the membership renewed every 4 years
subordinate courts:
high courts; district courts; hierarchy of administrative courts
Political parties and leaders:
Democratic Progressive Party or DPP [CHO Jung-tai] ++ Kuomintang or KMT (Nationalist Party) [WU Den-yih] ++ New Power Party or NPP [CHIU Hsien-chih] ++ Non-Partisan Solidarity Union or NPSU [LIN Pin-kuan] ++ People First Party or PFP [James SOONG Chu-yu]
International organization participation:
ADB (Taipei, China), APEC (Chinese Taipei), BCIE, IOC, ITUC (NGOs), SICA (observer), WTO (Taipei, China);
note - separate customs territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
none; commercial and cultural relations with its citizens in the US are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts, represented by Stanley KAO (since 5 June 2016); office: 4201 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20016; telephone: [1] 202 895-1800
Taipei Economic and Cultural Offices (branch offices):
Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Denver (CO), Houston, Honolulu, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission:
the US does not have an embassy in Taiwan; commercial and cultural relations with the people of Taiwan are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts; it is managed by Director William Brent CHRISTENSEN (since 11 August 2018); telephone [886] 7-335-5006; FAX [886] 7-338-0551
telephone:
(+886) (02) 2162-2000
branch office(s):
American Institute in Taiwan ++ No. 100, Jinhu Road, ++ Neihu District 11461, Taipei City
other offices:
Kaohsiung (Branch Office)
Flag description:
red field with a dark blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white sun with 12 triangular rays; the blue and white design of the canton (symbolizing the sun of progress) dates to 1895; it was later adopted as the flag of the Kuomintang Party; blue signifies liberty, justice, and democracy, red stands for fraternity, sacrifice, and nationalism, and white represents equality, frankness, and the people's livelihood; the 12 rays of the sun are those of the months and the twelve traditional Chinese hours (each ray equals two hours)
note: similar to the flag of Samoa
National symbol(s):
white, 12-rayed sun on blue field; national colors: blue, white, red
National anthem:
name:
"Zhonghua Minguo guoge" (National Anthem of the Republic of China)
lyrics/music:
HU Han-min, TAI Chi-t'ao, and LIAO Chung-k'ai/CHENG Mao-Yun
note: adopted 1930; also the song of the Kuomintang Party; it is informally known as "San Min Chu I" or "San Min Zhu Yi" (Three Principles of the People); because of political pressure from China, "Guo Qi Ge" (National Banner Song) is used at international events rather than the official anthem of Taiwan; the "National Banner Song" has gained popularity in Taiwan and is commonly used during flag raisings
Economy
Economic overview:
Taiwan has a dynamic capitalist economy that is driven largely by industrial manufacturing, and especially exports of electronics, machinery, and petrochemicals. This heavy dependence on exports exposes the economy to fluctuations in global demand. Taiwan's diplomatic isolation, low birth rate, rapidly aging population, and increasing competition from China and other Asia Pacific markets are other major long-term challenges.
++ Following the landmark Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) signed with China in June 2010, Taiwan in July 2013 signed a free trade deal with New Zealand - Taipei's first-ever with a country with which it does not maintain diplomatic relations - and, in November of that year, inked a trade pact with Singapore. However, follow-on components of the ECFA, including a signed agreement on trade in services and negotiations on trade in goods and dispute resolution, have stalled. In early 2014, the government bowed to public demand and proposed a new law governing the oversight of cross-Strait agreements, before any additional deals with China are implemented; the legislature has yet to vote on such legislation, leaving the future of ECFA uncertain. President TSAI since taking office in May 2016 has promoted greater economic integration with South and Southeast Asia through the New Southbound Policy initiative and has also expressed interest in Taiwan joining the Trans-Pacific Partnership as well as bilateral trade deals with partners such as the US. These overtures have likely played a role in increasing Taiwan's total exports, which rose 11% during the first half of 2017, buoyed by strong demand for semiconductors.
++ Taiwan's total fertility rate of just over one child per woman is among the lowest in the world, raising the prospect of future labor shortages, falling domestic demand, and declining tax revenues. Taiwan's population is aging quickly, with the number of people over 65 expected to account for nearly 20% of the island's total population by 2025.
++ The island runs a trade surplus with many economies, including China and the US, and its foreign reserves are the world's fifth largest, behind those of China, Japan, Saudi Arabia, and Switzerland. In 2006, China overtook the US to become Taiwan's second-largest source of imports after Japan. China is also the island's number one destination for foreign direct investment. Taiwan since 2009 has gradually loosened rules governing Chinese investment and has also secured greater market access for its investors on the mainland. In August 2012, the Taiwan Central Bank signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on cross-Strait currency settlement with its Chinese counterpart. The MOU allows for the direct settlement of Chinese renminbi (RMB) and the New Taiwan dollar across the Strait, which has helped Taiwan develop into a local RMB hub.
++ Closer economic links with the mainland bring opportunities for Taiwan's economy but also pose challenges as political differences remain unresolved and China's economic growth is slowing. President TSAI's administration has made little progress on the domestic economic issues that loomed large when she was elected, including concerns about stagnant wages, high housing prices, youth unemployment, job security, and financial security in retirement. TSAI has made more progress on boosting trade with South and Southeast Asia, which may help insulate Taiwan's economy from a fall in mainland demand should China's growth slow in 2018.
GDP real growth rate:
2.71%
(2019 est.)
2.75%
(2018 est.)
3.31%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
0.5%
(2019 est.)
1.3%
(2018 est.)
0.6%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
Credit ratings:
Fitch rating:
AA-
(2016)
Moody's rating:
Aa3
(1994)
Standard & Poors rating:
AA-
(2002)
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$1,143,277,000,000
(2019 est.)
$1,113,126,000,000
(2018 est.)
$1,083,384,000,000
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2010 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$611.391 billion
(2019 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$24,502
(2018 est.)
$50,500
(2017 est.)
$23,865
(2017 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 64
Gross national saving:
34.9% of GDP
(2017 est.)
35.5% of GDP
(2016 est.)
36.3% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 17
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
1.8%
(2017 est.)
industry:
36%
(2017 est.)
services:
62.1%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
53%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
14.1%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
20.5%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
-0.2%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
65.2%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-52.6%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
84.9
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
rice, vegetables, fruit, tea, flowers; pigs, poultry; fish
Industries:
electronics, communications and information technology products, petroleum refining, chemicals, textiles, iron and steel, machinery, cement, food processing, vehicles, consumer products, pharmaceuticals
Industrial production growth rate:
3.9%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 79
Labor force:
11.498 million
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
4.9%
industry:
35.9%
services:
59.2%
(2016 est.)
Unemployment rate:
3.73%
(2019 est.)
3.69%
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
Population below poverty line:
1.5%
(2012 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
6.4%
(2010)
highest 10%:
40.3%
(2010)
Budget:
revenues:
91.62 billion
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
92.03 billion
(2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
16% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 184
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-0.1% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
Public debt:
35.7% of GDP
(2017 est.)
36.2% of GDP
(2016 est.)
note: data for central government
country comparison to the world: 149
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Current account balance:
$65.173 billion
(2019 est.)
$70.843 billion
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
Exports:
$388.49 billion
(2019 est.)
$383.484 billion
(2018 est.)
$382.736 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
Exports - partners:
China 27.9%, US 14.1%, Hong Kong 12.3%, Japan 7.1%, Singapore 5.5%, South Korea 5.1%
(2019)
Exports - commodities:
semiconductors, petrochemicals, automobile/auto parts, ships, wireless communication equipment, flat display displays, steel, electronics, plastics, computers
Imports:
$308.744 billion
(2019 est.)
$305.428 billion
(2018 est.)
$303.067 billion
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 23
Imports - commodities:
oil/petroleum, semiconductors, natural gas, coal, steel, computers, wireless communication equipment, automobiles, fine chemicals, textiles
Imports - partners:
China 20.1%, Japan 15.4%, US 12.3%, South Korea 6.2%
(2019)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$456.7 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$439 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
Debt - external:
$181.9 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$172.2 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
Exchange rates:
New Taiwan dollars (TWD) per US dollar -
28.211
(2020 est.)
30.472
(2019 est.)
30.8395
(2018 est.)
31.911
(2014 est.)
30.363
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity - production:
246.1 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
Electricity - consumption:
237.4 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
Electricity - exports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
Electricity - imports:
0 kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
49.52 million kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
79% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 87
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
11% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
4% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
6% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 105
Crude oil - production:
196 bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 96
Crude oil - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
Crude oil - imports:
846,400 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 13
Crude oil - proved reserves:
2.38 million bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
Refined petroleum products - production:
924,000 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
962,400 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
Refined petroleum products - exports:
349,600 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
Refined petroleum products - imports:
418,300 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
Natural gas - production:
237.9 million cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
Natural gas - consumption:
22.45 billion cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
Natural gas - imports:
22.14 billion cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
Natural gas - proved reserves:
6.229 billion cu m
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 86
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
348.8 million Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
12,863,860
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
54.56
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
29,049,784
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
123.21
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
good telecommunications infrastructure and competitive mobile market; Taiwan has a stable regulatory system and an educated workforce building on availability of fixed and mobile broadband networks; investors attracted to this excellent telecom infrastructure; fixed-line will decline in the next 5 years; 6 mobile network operators; 4G LTE service; regulator begins multi-spectrum auction for 5G services; govt. to release NT $20.5 billion to encourage development of 5G services
(2020)
domestic:
fixed-line 55 per 100 and mobile-cellular 123 per 100
(2019)
international:
country code - 886; landing points for the EAC-C2C, APCN-2, FASTER, SJC2, TSE-1, TPE, APG, SeaMeWe-3, FLAG North Asia Loop/REACH North Asia Loop, HKA, NCP, and PLCN submarine fiber cables provide links throughout Asia, Australia, the Middle East, Europe, Africa and the US; satellite earth stations - 2
(2019)
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
5 nationwide television networks operating roughly 22 TV stations; more than 300 satellite TV channels are available; about 60% of households utilize multi-channel cable TV; 99.9% of households subscribe to digital cable TV; national and regional radio networks with about 171 radio stations
(2019)
Internet country code:
.tw
Internet users:
total:
21,845,944
percent of population:
92.78%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
5,725,022
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
24
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
Transportation
National air transport system:
number of registered air carriers:
7
(2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers:
216
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
B
(2016)
Airports:
37
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 107
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
35
(2013)
over 3,047 m:
8
(2013)
2,438 to 3,047 m:
7
(2013)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
10
(2013)
914 to 1,523 m:
8
(2013)
under 914 m:
2
(2013)
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
2
(2013)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
1
(2013)
under 914 m:
1
(2013)
Heliports:
31
(2013)
Pipelines:
25 km condensate, 2,200 km gas, 13,500 km oil
(2018)
Railways:
total:
1,613 km
(2018)
standard gauge:
345 km
1.435-m gauge (345 km electrified)
(2018)
narrow gauge:
1,118.1 km
1.067-m gauge (793.9 km electrified)
(2018)
150 0.762-m gauge
note: the 0.762-gauge track belongs to three entities: the Forestry Bureau, Taiwan Cement, and TaiPower
country comparison to the world: 81
Roadways:
total:
43,206 km
(2017)
paved:
42,793 km
(includes 1,348 km of highways and 737 km of expressways)
(2017)
unpaved:
413 km
(2017)
country comparison to the world: 88
Merchant marine:
total:
389
by type:
bulk carrier 30, container ship 47, general cargo 56, oil tanker 32, other 224
(2019)
country comparison to the world: 46
Ports and terminals:
major seaport(s):
Keelung (Chi-lung), Kaohsiung, Hualian, Taichung
container port(s) (TEUs):
Kaohsiung (10,271,018), Taichung (1,660,663), Taipei (1,561,743)
(2017)
LNG terminal(s) (import):
Yung An (Kaohsiung), Taichung
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Taiwan Armed Forces: Army, Navy (includes Marine Corps), Air Force, Military Police Command, Armed Forces Reserve Command; Taiwan Coast Guard Administration (a law enforcement organization with homeland security functions during peacetime and national defense missions during wartime)
(2020)
Military expenditures:
1.7% of GDP
(2019)
1.7% of GDP
(2018)
1.8% of GDP
(2017)
1.8% of GDP
(2016)
1.9% of GDP
(2015)
country comparison to the world: 66
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Taiwan military has approximately 170,000 active duty troops (90,000 Army; 40,000 Navy; 40,000 Air Force)
(2019)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
the Taiwan military is armed mostly with second-hand weapons and equipment provided by the US; Taiwan also has a domestic defense industry capable of upgrading some weapons systems and building surface naval craft and submarines
(2019)
Military service age and obligation:
starting with those born in 1994, males 18-36 years of age may volunteer for military service or must complete 4 months of compulsory military training (or substitute civil service in some cases); men born before December 1993 are required to complete compulsory service for 1 year (military or civil); men are subject to training recalls up to four times for periods not to exceed 20 days for 8 years after discharge; women may enlist, but are restricted to noncombat roles in most cases; as part of its transition to an all-volunteer military in December 2018, the last cohort of one-year military conscripts completed their service obligations
(2019)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
involved in complex dispute with Brunei, China, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Vietnam over the Spratly Islands, and with China and the Philippines over Scarborough Reef; the 2002 "Declaration on the Conduct of Parties in the South China Sea" has eased tensions but falls short of a legally binding "code of conduct" desired by several of the disputants; Paracel Islands are occupied by China, but claimed by Taiwan and Vietnam; in 2003, China and Taiwan became more vocal in rejecting both Japan's claims to the uninhabited islands of the Senkaku-shoto (Diaoyu Tai) and Japan's unilaterally declared exclusive economic zone in the East China Sea where all parties engage in hydrocarbon prospecting
Illicit drugs:
regional transit point for heroin, methamphetamine, and precursor chemicals; transshipment point for drugs to Japan; major problem with domestic consumption of methamphetamine and heroin; rising problems with use of ketamine and club drugs