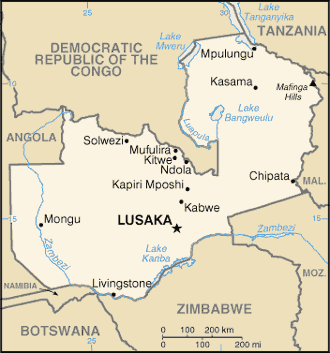
Zambia :: Africa
Introduction
Background:
Multiple waves of Bantu-speaking groups moved into and through what is now Zambia over the past thousand years. In the 1880s, the British began securing mineral and other economic concessions from various local leaders and the territory that is now Zambia eventually came under the control of the former British South Africa Company and was incorporated as the protectorate of Northern Rhodesia in 1911. Administrative control was taken over by the UK in 1924. During the 1920s and 1930s, advances in mining spurred development and immigration. ++ The name was changed to Zambia upon independence in 1964. In the 1980s and 1990s, declining copper prices, economic mismanagement, and a prolonged drought hurt the economy. Elections in 1991 brought an end to one-party rule and propelled the Movement for Multiparty Democracy (MMD) to government. The subsequent vote in 1996, however, saw increasing harassment of opposition parties and abuse of state media and other resources. The election in 2001 was marked by administrative problems, with three parties filing a legal petition challenging the election of ruling party candidate Levy MWANAWASA. MWANAWASA was reelected in 2006 in an election that was deemed free and fair. Upon his death in August 2008, he was succeeded by his vice president, Rupiah BANDA, who won a special presidential byelection later that year. The MMD and BANDA lost to the Patriotic Front (PF) and Michael SATA in the 2011 general elections. SATA, however, presided over a period of haphazard economic management and attempted to silence opposition to PF policies. SATA died in October 2014 and was succeeded by his vice president, Guy SCOTT, who served as interim president until January 2015, when Edgar LUNGU won the presidential byelection and completed SATA's term. LUNGU then won a full term in August 2016 presidential elections.
Geography
Location:
Southern Africa, east of Angola, south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Geographic coordinates:
15 00 S, 30 00 E
Map references:
Africa
Area:
total:
752,618 sq km
land:
743,398 sq km
water:
9,220 sq km
country comparison to the world: 40
Area - comparative:
almost five times the size of Georgia; slightly larger than Texas
Land boundaries:
total:
6,043.15 km
border countries (8):
Angola 1065 km, Botswana 0.15 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 2332 km, Malawi 847 km, Mozambique 439 km, Namibia 244 km, Tanzania 353 km, Zimbabwe 763 km
Coastline:
0 km
(landlocked)
Maritime claims:
none (landlocked)
Climate:
tropical; modified by altitude; rainy season (October to April)
Terrain:
mostly high plateau with some hills and mountains
Elevation:
mean elevation:
1,138 m
lowest point:
Zambezi river 329 m
highest point:
unnamed elevation in Mafinga Hills 2,301 m
Natural resources:
copper, cobalt, zinc, lead, coal, emeralds, gold, silver, uranium, hydropower
Land use:
agricultural land:
31.7%
(2011 est.)
arable land:
4.8%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent crops:
0%
(2011 est.)
/
permanent pasture:
26.9%
(2011 est.)
forest:
66.3%
(2011 est.)
other:
2%
(2011 est.)
Irrigated land:
1,560 sq km
(2012)
Population distribution:
one of the highest levels of urbanization in Africa; high density in the central area, particularly around the cities of Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe, and Mufulira as shown in this population distribution map
Natural hazards:
periodic drought; tropical storms (November to April)
Environment - current issues:
air pollution and resulting acid rain in the mineral extraction and refining region; chemical runoff into watersheds; loss of biodiversity; poaching seriously threatens rhinoceros, elephant, antelope, and large cat populations; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification; lack of adequate water treatment presents human health risks
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
Geography - note:
landlocked; the Zambezi forms a natural riverine boundary with Zimbabwe; Lake Kariba on the Zambia-Zimbabwe border forms the world's largest reservoir by volume (180 cu km; 43 cu mi)
People and Society
Population:
17,426,623
(July 2020 est.)
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected
country comparison to the world: 66
Nationality:
noun:
Zambian(s)
adjective:
Zambian
Ethnic groups:
Bemba 21%, Tonga 13.6%, Chewa 7.4%, Lozi 5.7%, Nsenga 5.3%, Tumbuka 4.4%, Ngoni 4%, Lala 3.1%, Kaonde 2.9%, Namwanga 2.8%, Lunda (north Western) 2.6%, Mambwe 2.5%, Luvale 2.2%, Lamba 2.1%, Ushi 1.9%, Lenje 1.6%, Bisa 1.6%, Mbunda 1.2%, other 13.8%, unspecified 0.4%
(2010 est.)
Languages:
Bemba 33.4%, Nyanja 14.7%, Tonga 11.4%, Lozi 5.5%, Chewa 4.5%, Nsenga 2.9%, Tumbuka 2.5%, Lunda (North Western) 1.9%, Kaonde 1.8%, Lala 1.8%, Lamba 1.8%, English (official) 1.7%, Luvale 1.5%, Mambwe 1.3%, Namwanga 1.2%, Lenje 1.1%, Bisa 1%, other 9.7%, unspecified 0.2%
(2010 est.)
note: Zambia is said to have over 70 languages, although many of these may be considered dialects; all of Zambia's major languages are members of the Bantu family; Chewa and Nyanja are mutually intelligible dialects
Religions:
Protestant 75.3%, Roman Catholic 20.2%, other 2.7% (includes Muslim Buddhist, Hindu, and Baha'i), none 1.8%
(2010 est.)
Demographic profile:
Zambia's poor, youthful population consists primarily of Bantu-speaking people representing nearly 70 different ethnicities. Zambia's high fertility rate continues to drive rapid population growth, averaging almost 3 percent annually between 2000 and 2010. The country's total fertility rate has fallen by less than 1.5 children per woman during the last 30 years and still averages among the world's highest, almost 6 children per woman, largely because of the country's lack of access to family planning services, education for girls, and employment for women. Zambia also exhibits wide fertility disparities based on rural or urban location, education, and income. Poor, uneducated women from rural areas are more likely to marry young, to give birth early, and to have more children, viewing children as a sign of prestige and recognizing that not all of their children will live to adulthood. HIV/AIDS is prevalent in Zambia and contributes to its low life expectancy.
++ Zambian emigration is low compared to many other African countries and is comprised predominantly of the well-educated. The small amount of brain drain, however, has a major impact in Zambia because of its limited human capital and lack of educational infrastructure for developing skilled professionals in key fields. For example, Zambia has few schools for training doctors, nurses, and other health care workers. Its spending on education is low compared to other Sub-Saharan countries.
Age structure:
0-14 years:
45.74%
(male 4,005,134/female 3,964,969)
15-24 years:
20.03%
(male 1,744,843/female 1,746,561)
25-54 years:
28.96%
(male 2,539,697/female 2,506,724)
55-64 years:
3.01%
(male 242,993/female 280,804)
65 years and over:
2.27%
(male 173,582/female 221,316)
(2020 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio:
85.7
youth dependency ratio:
81.7
elderly dependency ratio:
4
potential support ratio:
25.3
(2020 est.)
Median age:
total:
16.9 years
male:
16.7 years
female:
17 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 220
Population growth rate:
2.89%
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
Birth rate:
40.4 births/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
Death rate:
11.6 deaths/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
Net migration rate:
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 97
Population distribution:
one of the highest levels of urbanization in Africa; high density in the central area, particularly around the cities of Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe, and Mufulira as shown in this population distribution map
Urbanization:
urban population:
44.6% of total population
(2020)
rate of urbanization:
4.23% annual rate of change
(2015-20 est.)
Major urban areas - population:
2.774 million LUSAKA (capital)
(2020)
Sex ratio:
at birth:
1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
15-24 years:
1 male(s)/female
25-54 years:
1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years:
0.87 male(s)/female
65 years and over:
0.78 male(s)/female
total population:
1 male(s)/female
(2020 est.)
Mother's mean age at first birth:
19.2 years
(2013/14 est.)
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29
Maternal mortality rate:
213 deaths/100,000 live births
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
Infant mortality rate:
total:
56 deaths/1,000 live births
male:
61.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female:
50.7 deaths/1,000 live births
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
Life expectancy at birth:
total population:
53.6 years
male:
51.9 years
female:
55.3 years
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 225
Total fertility rate:
5.49 children born/woman
(2020 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
Contraceptive prevalence rate:
49.5%
(2018)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban:
89.5% of population
rural:
50.9% of population
total:
67.5% of population
unimproved:
urban:
10.5% of population
rural:
49.1% of population
total:
32.5% of population
(2017 est.)
Current Health Expenditure:
4.5%
(2017)
Physicians density:
0.16 physicians/1,000 population
(2016)
Hospital bed density:
2 beds/1,000 population
(2010)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban:
69.6% of population
rural:
24.8% of population
total:
44.1% of population
unimproved:
urban:
31.4% of population
rural:
75.2% of population
total:
55.9% of population
(2017 est.)
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
12.1%
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 8
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
1.2 million
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
17,000
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
Major infectious diseases:
degree of risk:
very high
(2020)
food or waterborne diseases:
bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne diseases:
malaria and dengue fever
water contact diseases:
schistosomiasis
animal contact diseases:
rabies
Obesity - adult prevalence rate:
8.1%
(2016)
country comparison to the world: 155
Children under the age of 5 years underweight:
11.8%
(2018/19)
country comparison to the world: 55
Education expenditures:
4.6% of GDP
NA
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 76
Literacy:
definition:
age 15 and over can read and write English
total population:
86.7%
male:
90.6%
female:
83.1%
(2018)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total:
24%
male:
23.6%
female:
24.4%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
Government
Country name:
conventional long form:
Republic of Zambia
conventional short form:
Zambia
former:
Northern Rhodesia
etymology:
name derived from the Zambezi River, which flows through the western part of the country and forms its southern border with neighboring Zimbabwe
Government type:
presidential republic
Capital:
name:
Lusaka; note - a proposal to build a new capital city in Ngabwe was announced in May 2017
geographic coordinates:
15 25 S, 28 17 E
time difference:
UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: named after a village called Lusaka, located at Manda Hill, near where Zambia's National Assembly building currently stands; the village was named after a headman (chief) Lusakasa
Administrative divisions:
10 provinces; Central, Copperbelt, Eastern, Luapula, Lusaka, Muchinga, Northern, North-Western, Southern, Western
Independence:
24 October 1964 (from the UK)
National holiday:
Independence Day, 24 October (1964)
Constitution:
history:
several previous; latest adopted 24 August 1991, promulgated 30 August 1991
amendments:
proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly in two separate readings at least 30 days apart; passage of amendments affecting fundamental rights and freedoms requires approval by at least one half of votes cast in a referendum prior to consideration and voting by the Assembly; amended 1996, 2015, 2016
Legal system:
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Citizenship:
citizenship by birth:
only if at least one parent is a citizen of Zambia
citizenship by descent only:
yes, if at least one parent was a citizen of Zambia
dual citizenship recognized:
yes
residency requirement for naturalization:
5 years for those with an ancestor who was a citizen of Zambia, otherwise 10 years residency is required
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state:
President Edgar LUNGU (since 25 January 2015); Vice President Inonge WINA (since 26 January 2015); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government:
President Edgar LUNGU (since 25 January 2015); Vice President Inonge WINA (since 26 January 2015)
cabinet:
Cabinet appointed by president from among members of the National Assembly
elections/appointments:
president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); last held on 11 August 2016 (next to be held in 2021)
election results:
Edgar LUNGU reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Edgar LUNGU (PF) 50.4%, Hakainde HICHILEMA (UPND) 47.6%, other 2.0%
Legislative branch:
description:
unicameral National Assembly (165 seats; 156 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote in 2 rounds if needed, and up to 8 appointed by the president; members serve 5-year terms); note - 6 additional electoral seats were added for the 11 August 2016 election, up from 150 electoral seats in the 2011 election
elections:
last held on 11 August 2016 (next to be held in 2021)
election results:
percent of vote by party - PF 42%, UPND 41.7%, MMD 2.7%, FDD 2.2%, other 1.9%,independent 9.5%; seats by party - PF 89, UPND 54, MMD 5, FDD 1, NDC 1, independent 14; composition - men 135, women 30, percent of women 18.2%
Judicial branch:
highest courts:
Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice, deputy chief justice, and at least 11 judges); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 11 judges); note - the Constitutional Court began operation in June 2016
judge selection and term of office:
Supreme Court and Constitutional Court judges appointed by the president of the republic upon the advice of the 9-member Judicial Service Commission, which is headed by the chief justice, and ratified by the National Assembly; judges normally serve until age 65
subordinate courts:
Court of Appeal; High Court; Industrial Relations Court; subordinate courts (3 levels, based on upper limit of money involved); Small Claims Court; local courts (2 grades, based on upper limit of money involved)
Political parties and leaders:
Alliance for Democracy and Development or ADD [Charles MILUPI] ++ Forum for Democracy and Development or FDD [Edith NAWAKWI] ++ Movement for Multiparty Democracy or MMD [Felix MUTATI] ++ National Democratic Congress or NDC [Chishimba KAMBWILI] ++ Patriotic Front or PF [Edgar LUNGU] ++ United Party for National Development or UPND [Hakainde HICHILEMA]
International organization participation:
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission:
Ambassador Lazarous KAPAMBWE (since 8 April 2020)
chancery:
2200 R Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone:
[1] (202) 265-9717 through 9719
FAX:
[1] (202) 332-0826
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission:
Charge d'Affaires David J. YOUNG (since 2 March 2020)
telephone:
[260] (0) 211-357-000 ++
embassy:
Eastern end of Kabulonga Road, Ibex Hill, Lusaka
mailing address:
P. O. Box 320065, Lusaka
FAX:
[260] 211-357-224
Flag description:
green field with a panel of three vertical bands of red (hoist side), black, and orange below a soaring orange eagle, on the outer edge of the flag; green stands for the country's natural resources and vegetation, red symbolizes the struggle for freedom, black the people of Zambia, and orange the country's mineral wealth; the eagle represents the people's ability to rise above the nation's problems
National symbol(s):
African fish eagle; national colors: green, red, black, orange
National anthem:
name:
"Lumbanyeni Zambia" (Stand and Sing of Zambia, Proud and Free)
lyrics/music:
multiple/Enoch Mankayi SONTONGA
note: adopted 1964; the melody, from the popular song "God Bless Africa," is the same as that of Tanzania but with different lyrics; the melody is also incorporated into South Africa's anthem
Economy
Economic overview:
Zambia had one of the world's fastest growing economies for the ten years up to 2014, with real GDP growth averaging roughly 6.7% per annum, though growth slowed during the period 2015 to 2017, due to falling copper prices, reduced power generation, and depreciation of the kwacha. Zambia's lack of economic diversification and dependency on copper as its sole major export makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in the world commodities market and prices turned downward in 2015 due to declining demand from China; Zambia was overtaken by the Democratic Republic of Congo as Africa's largest copper producer. GDP growth picked up in 2017 as mineral prices rose.
++ Despite recent strong economic growth and its status as a lower middle-income country, widespread and extreme rural poverty and high unemployment levels remain significant problems, made worse by a high birth rate, a relatively high HIV/AIDS burden, by market-distorting agricultural and energy policies, and growing government debt. Zambia raised $7 billion from international investors by issuing separate sovereign bonds in 2012, 2014, and 2015. Concurrently, it issued over $4 billion in domestic debt and agreed to Chinese-financed infrastructure projects, significantly increasing the country's public debt burden to more than 60% of GDP. The government has considered refinancing $3 billion worth of Eurobonds and significant Chinese loans to cut debt servicing costs.
GDP real growth rate:
3.4%
(2017 est.)
3.8%
(2016 est.)
2.9%
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
9.1%
(2019 est.)
7.4%
(2018 est.)
6.5%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
Credit ratings:
Fitch rating:
RD
(2020)
Moody's rating:
Ca
(2020)
Standard & Poors rating:
SD
(2020)
GDP (purchasing power parity) - real:
$68.93 billion
(2017 est.)
$66.66 billion
(2016 est.)
$64.25 billion
(2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$25.71 billion
(2017 est.)
GDP - per capita (PPP):
$4,000
(2017 est.)
$4,000
(2016 est.)
$4,000
(2015 est.)
note: data are in 2017 dollars
country comparison to the world: 165
Gross national saving:
38.3% of GDP
(2017 est.)
37.3% of GDP
(2016 est.)
38.9% of GDP
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
GDP - composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture:
7.5%
(2017 est.)
industry:
35.3%
(2017 est.)
services:
57%
(2017 est.)
GDP - composition, by end use:
household consumption:
52.6%
(2017 est.)
government consumption:
21%
(2017 est.)
investment in fixed capital:
27.1%
(2017 est.)
investment in inventories:
1.2%
(2017 est.)
exports of goods and services:
43%
(2017 est.)
imports of goods and services:
-44.9%
(2017 est.)
Ease of Doing Business Index scores:
56.9
(2020)
Agriculture - products:
corn, sorghum, rice, peanuts, sunflower seeds, vegetables, flowers, tobacco, cotton, sugarcane, cassava (manioc, tapioca), coffee; cattle, goats, pigs, poultry, milk, eggs, hides
Industries:
copper mining and processing, emerald mining, construction, foodstuffs, beverages, chemicals, textiles, fertilizer, horticulture
Industrial production growth rate:
4.7%
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
Labor force:
6.898 million
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
Labor force - by occupation:
agriculture:
54.8%
industry:
9.9%
services:
35.3%
(2017 est.)
Unemployment rate:
15%
(2008 est.)
50%
(2000 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
Population below poverty line:
54.4%
(2015 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%:
1.5%
highest 10%:
47.4%
(2010)
Budget:
revenues:
4.473 billion
(2017 est.)
expenditures:
6.357 billion
(2017 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
17.4% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-7.3% (of GDP)
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
Public debt:
63.1% of GDP
(2017 est.)
60.7% of GDP
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Current account balance:
-$1.006 billion
(2017 est.)
-$934 million
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 145
Exports:
$8.216 billion
(2017 est.)
$6.514 billion
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 106
Exports - partners:
Switzerland 44.8%, China 16.1%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 6.2%, Singapore 6%, South Africa 5.9%
(2017)
Exports - commodities:
copper/cobalt, cobalt, electricity; tobacco, flowers, cotton
Imports:
$7.852 billion
(2017 est.)
$6.539 billion
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
Imports - commodities:
machinery, transportation equipment, petroleum products, electricity, fertilizer, foodstuffs, clothing
Imports - partners:
South Africa 28.2%, Democratic Republic of the Congo 20.8%, China 12.9%, Kuwait 5.4%, UAE 4.6%
(2017)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$2.082 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$2.353 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
Debt - external:
$11.66 billion
(31 December 2017 est.)
$9.562 billion
(31 December 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
Exchange rates:
Zambian kwacha (ZMK) per US dollar -
21.065
(2020 est.)
15.3736
(2019 est.)
11.855
(2018 est.)
8.6
(2014 est.)
6.2
(2013 est.)
Energy
Electricity access:
population without electricity:
11 million
(2019)
electrification - total population:
37%
(2019)
electrification - urban areas:
76%
(2019)
electrification - rural areas:
6%
(2019)
Electricity - production:
11.55 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
Electricity - consumption:
11.04 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
Electricity - exports:
1.176 billion kWh
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
Electricity - imports:
2.185 billion kWh
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
Electricity - installed generating capacity:
2.573 million kW
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
Electricity - from fossil fuels:
5% of total installed capacity
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 204
Electricity - from nuclear fuels:
0% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:
93% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
Electricity - from other renewable sources:
2% of total installed capacity
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
Crude oil - production:
0 bbl/day
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 218
Crude oil - exports:
0 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 216
Crude oil - imports:
12,860 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 70
Crude oil - proved reserves:
0 bbl
(1 January 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 213
Refined petroleum products - production:
13,120 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 98
Refined petroleum products - consumption:
23,000 bbl/day
(2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
Refined petroleum products - exports:
371 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
Refined petroleum products - imports:
10,150 bbl/day
(2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
Natural gas - production:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 215
Natural gas - consumption:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
Natural gas - exports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
Natural gas - imports:
0 cu m
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 214
Natural gas - proved reserves:
0 cu m
(1 January 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 208
Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:
3.777 million Mt
(2017 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
Communications
Telephones - fixed lines:
total subscriptions:
91,422
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 140
Telephones - mobile cellular:
total subscriptions:
16,322,168
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
96.41
(2019 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
Telecommunication systems:
general assessment:
service is among the best in Sub-Saharan Africa; regulatory promotes competition and is a partner to private sector service providers, offering mobile voice and Internet at some of the lowest prices in the region; investment made in data centers, education centers and computer assembly training plants; operators invest in 3G and LTE-based services; Chinese company Huawei is helping to upgrade state-owned mobile infrastructure for 5G services; 3 cellular telephone providers currently in operation, plus several data only ISPs; 1,010 towers project to soon be completed
(2020)
domestic:
fiber optic connections are available between most larger towns and cities with microwave radio relays serving more rural areas; 3G and LTE with FttX in limited urban areas and private Ku or Ka band VSAT terminals in remote locations; fixed-line 1 per 100 and mobile-cellular 96 per 100
(2019)
international:
country code - 260; multiple providers operate overland fiber optic routes via Zimbabwe/South Africa, Botswana/Namibia and Tanzania provide access to the major undersea cables
note: the COVID-19 outbreak is negatively impacting telecommunications production and supply chains globally; consumer spending on telecom devices and services has also slowed due to the pandemic's effect on economies worldwide; overall progress towards improvements in all facets of the telecom industry - mobile, fixed-line, broadband, submarine cable and satellite - has moderated
Broadcast media:
according to the Independent Broadcast Authority, there are 137 radio stations and 47 television stations in Zambia; out of the 137 radio stations, 133 are private (categorized as either commercial or community radio stations), while 4 are public-owned; state-owned Zambia National Broadcasting Corporation (ZNBC) operates 2 television channels and 3 radio stations; ZNBC owns 75% shares in GoTV, 40% in MultiChoice, and 40% in TopStar Communications Company, all of which operate in-country
(2019)
Internet country code:
.zm
Internet users:
total:
2,351,646
percent of population:
14.3%
(July 2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
Broadband - fixed subscriptions:
total:
43,365
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants:
less than 1
(2018 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
Transportation
National air transport system:
number of registered air carriers:
3
(2020)
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers:
6
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers:
8,904
(2018)
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers:
75.08 million
mt-km
(2018)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix:
9J
(2016)
Airports:
88
(2013)
country comparison to the world: 64
Airports - with paved runways:
total:
8
(2013)
over 3,047 m:
1
(2013)
2,438 to 3,047 m:
3
(2013)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
3
(2013)
914 to 1,523 m:
1
(2013)
Airports - with unpaved runways:
total:
80
(2013)
2,438 to 3,047 m:
1
(2013)
1,524 to 2,437 m:
5
(2013)
914 to 1,523 m:
53
(2013)
under 914 m:
21
(2013)
Pipelines:
771 km oil
(2013)
Railways:
total:
3,126 km
(2014)
narrow gauge:
3,126 km
1.067-m gauge
(2014)
note: includes 1,860 km of the Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (TAZARA)
country comparison to the world: 59
Roadways:
total:
67,671 km
(2018)
paved:
14,888 km
(2018)
unpaved:
52,783 km
(2018)
country comparison to the world: 72
Waterways:
2,250 km
(includes Lake Tanganyika and the Zambezi and Luapula Rivers)
(2010)
country comparison to the world: 38
Merchant marine:
total:
1
by type:
other 1
(2019)
country comparison to the world: 182
Ports and terminals:
river port(s):
Mpulungu (Zambezi)
Military and Security
Military and security forces:
Zambia Defense Force (ZDF): Zambia Army, Zambia Air Force, Zambia National Service (support organization); the Zambia Police includes a paramilitary battalion
(2019)
Military expenditures:
1.2% of GDP
(2019)
1.3% of GDP
(2018)
1.3% of GDP
(2017)
1.4% of GDP
(2016)
1.8% of GDP
(2015)
country comparison to the world: 108
Military and security service personnel strengths:
the Zambia Defense Force (ZDF) has an estimated 17,000 active troops (15,500 Army; 1,500 Air); 1,400 paramilitary Police
(2019 est.)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions:
the ZDF's inventory is largely comprised of Soviet-era and older Chinese- and Russian-origin equipment; since 2010, China is the leading supplier of arms to Zambia
(2019 est.)
Military deployments:
920 Central African Republic (MINUSCA)
(2020)
Military service age and obligation:
18-25 years of age for male and female voluntary military service; no conscription; 12-year enlistment period (7 years active, 5 in the Reserves)
(2019)
Transnational Issues
Disputes - international:
in 2004, Zimbabwe dropped objections to plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River, thereby de facto recognizing a short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary in the river
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
refugees (country of origin):
55,523 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (refugees and asylum seekers), 18,815 (Angola), 7,997 (Burundi), 5,982 (Rwanda) (2020)
Illicit drugs:
transshipment point for moderate amounts of methaqualone, small amounts of heroin, and cocaine bound for southern Africa and possibly Europe; a poorly developed financial infrastructure coupled with a government commitment to combating money laundering make it an unattractive venue for money launderers; major consumer of cannabis